![]() Miricetina
Miricetina
Media gradimento : 8
| Valutazione | N. Esperti | Valutazione | N. Esperti |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | ||
| 2 | 7 | ||
| 3 | 8 | ||
| 4 | 9 | ||
| 5 | 10 |
Pro:
Possibile antitumorale - Seno (1) Cardioprotettivo (1) Neuroprotettivo (1) Antinfiammatorio (1) Protettivo della prostata (1)0 pt da admin
| Iscriviti per poter valutare questo oggetto, le sue recensioni e per contribuire a Tiiips.Valuta | Dove si trova? |
| "Descrizione" su Miricetina di admin (19537 pt) | 30-set-2024 16:51 |
| Leggi il Tiiip completo | (Invia il tuo commento) |
La miricetina è un flavonoide naturale presente in vari frutti, verdure, tè, bacche, vino rosso e piante, uva, cipolle. È conosciuta per le sue potenti proprietà antiossidanti, antinfiammatorie e potenzialmente anticancerogene. Nelle formulazioni cosmetiche, la miricetina è apprezzata per la sua capacità di proteggere la pelle dallo stress ossidativo, ridurre l'infiammazione e migliorare la salute della pelle nel complesso. La sua incorporazione nei prodotti per la cura della pelle aiuta a promuovere un aspetto più luminoso e giovanile.
Composizione Chimica e Struttura
La miricetina è caratterizzata da:
- Formula Chimica: C15H10O7
- Struttura: Un flavonolo con una struttura complessa costituita da uno scheletro di flavone con più gruppi idrossilici (-OH), che contribuiscono alla sua attività antiossidante.
La struttura unica della miricetina le consente di neutralizzare efficacemente i radicali liberi e fornire vari benefici per la salute.
Proprietà Fisiche
Aspetto: Tipicamente una polvere cristallina da gialla a arancione.
Solubilità: Solubile in solventi organici; leggermente solubile in acqua.
Punto di Fusione: Generalmente fonde a circa 305–308°C (581–586°F).
Odore: Inodore.
Stabilità: Stabile in condizioni normali di conservazione; deve essere protetta da calore eccessivo e luce.
Processo di Produzione
Estrazione: La miricetina viene estratta da fonti vegetali utilizzando metodi come l'estrazione con solvente o la distillazione a vapore per ottenere il flavonoide in forma concentrata.
Purificazione: L'estratto viene purificato per rimuovere impurità e garantire un prodotto di alta qualità.
Formulazione: La miricetina purificata viene incorporata in vari prodotti cosmetici per migliorarne le proprietà antiossidanti e protettive.
Applicazioni
- Medicina: Esplorata per i suoi potenziali effetti terapeutici in varie applicazioni legate alla salute (1), inclusa la sua funzione nel trattamento del cancro, cancro al seno (2), come antinfiammatorio (3), cardioprotettivo (4), come contrasto alla progressione delle cellule tumorali della prostata (5) e come neuroprotettivo (6)
Cosmetici: Comunemente utilizzata in creme, sieri e lozioni per i suoi benefici antiossidanti e antinfiammatori. Aiuta a calmare la pelle irritata, ridurre il rossore e migliorare la salute della pelle nel complesso.
Funzioni INCI:
Agente antiossidante. Ingrediente che contrasta lo stress ossidativo e che evita danni cellulari. I radicali liberi, i processi infiammatori patologici, le specie reattive dell'azoto e le specie reattive dell'ossigeno sono responsabili del processo di invecchiamento e di molte malattie causate dall'ossidazione.
Agente condizionante per capelli. Nelle formulazioni di shampoo per capelli possono coesistere una quantità rilevante di ingredienti con scopi specifici e mirati: detergenti, condizionanti, addensanti, opacizzanti, sequestranti, fragranze, conservanti, additivi particolari. Tuttavia gli ingredienti indispensabili sono i detergenti ed i condizionanti in quanto necessari e sufficienti per la pulizia e la gestibilità dei capelli. Gli altri hanno funzioni accessorie commerciali e non indispensabili come: aspetto estetico, profumo, colorazione ecc. Gli agenti condizionanti per i capelli hanno il compito di aumentarne la lucentezza, la maneggevolezza ed il volume, ridurne l'elettricità statica soprattutto dopo trattamenti quali colorazione, stiratura, ondulazione, asciugatura e spazzolatura. Sono, in pratica, dispersori che possono contenere tensioattivi cationici, addensanti, emollienti, polimeri. La tipologia degli agenti condizionatori per capelli comprende: condizionatori intensivi, condizionatori istantanei, condizionatori addensanti, condizionatori per l'asciugatura. Possono svolgere il loro compito generalmente accompagnati da altri diversi ingredienti.
CAS 529-44-2
EC number 208-463-2
Integratori Alimentari: Talvolta inclusa negli integratori per le sue proprietà antiossidanti.
Considerazioni Ambientali e di Sicurezza
La miricetina è generalmente considerata sicura per l'uso nei cosmetici quando applicata secondo le linee guida raccomandate. È ben tollerata dalla maggior parte dei tipi di pelle, comprese le pelli sensibili.
Pratiche di approvvigionamento e formulazione responsabili sono essenziali per garantire che l'ingrediente sia privo di contaminanti nocivi e prodotto in modo sostenibile.
 |  |
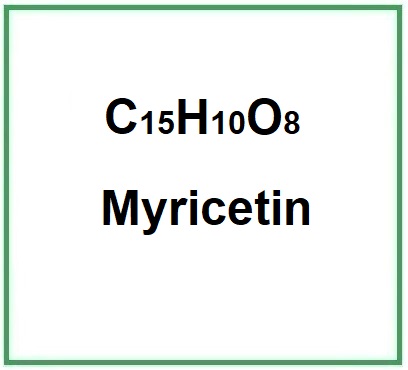
Molecular Formula C15H10O8
Molecular Weight 318.23 g/mol
CAS 529-44-2
UNII 76XC01FTOJ
EC Number 208-463-2
DTXSID8022400
Synonyms:
Myricitin
Myricetol
Bibliografia__________________________________________________________________________
(1) Felice MR, Maugeri A, De Sarro G, Navarra M, Barreca D. Molecular Pathways Involved in the Anti-Cancer Activity of Flavonols: A Focus on Myricetin and Kaempferol. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 16;23(8):4411. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084411.
Abstract. Natural compounds have always represented valuable allies in the battle against several illnesses, particularly cancer. In this field, flavonoids are known to modulate a wide panel of mechanisms involved in tumorigenesis, thus rendering them worthy candidates for both cancer prevention and treatment. In particular, it was reported that flavonoids regulate apoptosis, as well as hamper migration and proliferation, crucial events for the progression of cancer. In this review, we collect recent evidence concerning the anti-cancer properties of the flavonols myricetin and kaempferol, discussing their mechanisms of action to give a thorough overview of their noteworthy capabilities, which are comparable to those of their most famous analogue, namely quercetin. On the whole, these flavonols possess great potential, and hence further study is highly advised to allow a proper definition of their pharmaco-toxicological profile and assess their potential use in protocols of chemoprevention and adjuvant therapies.
(2) Lu Y, Sun J, Yang M, Xing Y, Zhu W, Zhu J, Ma X, Wang Y, Wang L, Jia Y. Myricetin Induces Ferroptosis and Inhibits Gastric Cancer Progression by Targeting NOX4. J Agric Food Chem. 2024 Mar 27;72(12):6178-6188. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c05243.
Abstract. Ferroptosis holds great potential as a therapeutic approach for gastric cancer (GC), a prevalent and deadly malignant tumor associated with high rates of incidence and mortality. Myricetin, well-known for its multifaceted biomedical attributes, particularly its anticancer properties, has yet to be thoroughly investigated regarding its involvement in ferroptosis. The aim of this research was to elucidate the impact of myricetin on ferroptosis in GC progression. The present study observed that myricetin could trigger ferroptosis in GC cells by enhancing malondialdehyde production and Fe2+ accumulation while suppressing glutathione levels. Mechanistically, myricetin directly interacted with NADPH oxidase 4 (NOX4), influencing its stability by inhibiting its ubiquitin degradation. Moreover, myricetin regulated the inhibition of ferroptosis induced by Helicobacter pylori cytotoxin-associated gene A (CagA) through the NOX4/NRF2/GPX4 pathway. In vivo experiments demonstrated that myricetin treatment significantly inhibited the growth of subcutaneous tumors in BALB/c nude mice. It was accompanied by increased NOX4 expression in tumor tissue and suppression of the NRF2/GPX4 antioxidant pathway. Therefore, this research underscores myricetin as a novel inducer of ferroptosis in GC cells through its interaction with NOX4. It is a promising candidate for GC treatment.
Soleimani M, Sajedi N. Myricetin Apoptotic Effects on T47D Breast Cancer Cells is a P53-Independent Approach. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020 Dec 1;21(12):3697-3704. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.12.3697.
Abstract. Objective: Using nutraceuticals in cancer therapy is a strategy contributing with other approaches to promote apoptosis in cancer cells. Myricetin is a polyphenol flavonoid that forms main ingredients of various type of foods and beverages. The inducing properties of myricetin in apoptosis is reported by several investigations. The present study aimed to assess apoptotic effects of myricetin on T47D breast cancer cells and to evaluate part of the mechanisms of action.....Conclusion: Myricetin enhances apoptosis in T47D breast cancer cells by evoking both extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathways. myricetin may practices its apoptotic properties on T47D cells through inducing BRCA1- GADD45 pathway.
(3) Sun WL, Li XY, Dou HY, Wang XD, Li JD, Shen L, Ji HF. Myricetin supplementation decreases hepatic lipid synthesis and inflammation by modulating gut microbiota. Cell Rep. 2021 Aug 31;36(9):109641. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109641.
(4) Wang L, Wu H, Yang F, Dong W. The Protective Effects of Myricetin against Cardiovascular Disease. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2019;65(6):470-476. doi: 10.3177/jnsv.65.470.
Abstract. Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death globally, except Africa, and poses a severe health burden worldwide. Both in vitro and in vivo studies have demonstrated the protective effects of myricetin for preventing CVD. For this review, we have assessed the literature from 2009 to 2019 at home and abroad to uncover the protective roles of myricetin for preventing CVD. Myricetin exhibits cardioprotective, anti-hypertensive, anti-atherosclerotic, anti-hyperglycemic, and anti-hyperlipidemic effects. In addition, myricetin may alleviate some of the complications caused by adult-onset diabetes. The combined functions of myricetin allow for the prevention of CVD. This review describes the possible therapeutic benefits of myricetin, along with its potential mechanisms of action, to support the clinical use of the myricetin for the prevention of CVD.
(5) Crocetto F, di Zazzo E, Buonerba C, Aveta A, Pandolfo SD, Barone B, Trama F, Caputo VF, Scafuri L, Ferro M, Cosimato V, Fusco F, Imbimbo C, Di Lorenzo G. Kaempferol, Myricetin and Fisetin in Prostate and Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Nutrients. 2021 Oct 23;13(11):3750. doi: 10.3390/nu13113750.
Abstract. Prostate and bladder cancer represent the two most frequently diagnosed genito-urinary malignancies. Diet has been implicated in both prostate and bladder cancer. Given their prolonged latency and high prevalence rates, both prostate and bladder cancer represent attractive candidates for dietary preventive measures, including the use of nutritional supplements. Flavonols, a class of flavonoids, are commonly found in fruit and vegetables and are known for their protective effect against diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Furthermore, a higher dietary intake of flavonols was associated with a lower risk of both bladder and prostate cancer in epidemiological studies. In this systematic review, we gathered all available evidence supporting the anti-cancer potential of selected flavonols (kaempferol, fisetin and myricetin) against bladder and prostate cancer. A total of 21, 15 and 7 pre-clinical articles on bladder or prostate cancer reporting on kaempferol, fisetin and myricetin, respectively, were found, while more limited evidence was available from animal models and epidemiological studies or clinical trials. In conclusion, the available evidence supports the potential use of these flavonols in prostate and bladder cancer, with a low expected toxicity, thus providing the rationale for clinical trials that explore dosing, settings for clinical use as well as their use in combination with other pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions.
(6) Gupta G, Siddiqui MA, Khan MM, Ajmal M, Ahsan R, Rahaman MA, Ahmad MA, Arshad M, Khushtar M. Current Pharmacological Trends on Myricetin. Drug Res (Stuttg). 2020 Oct;70(10):448-454. doi: 10.1055/a-1224-3625.
Abstract. Myricetin is a member of the group of flavonoids called flavonols. Myricetin is obtained from various fruit, vegetables, tea, berries and red wine. Myricetin is characterized by the pysrogallol B-ring, and the more hydroxylated structure is known to be capable for its increased biological properties compared with other flavonols. Myricetin is produced by the Myricaceae, Anacardiaceae, Polygonaceae, Pinaceae and Primulacea families. It is soluble in organic solvent such as ethanol, DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide), and dimethyl formamide (DMF). It is sparingly soluble in aqueous buffers. Myricetin shows its various pharmacological activities including antioxidant, anti-amyloidogenic, antibacterial, antiviral, antidiabetic, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, anti-epileptic and anti-ulcer. This review article focuses on pharmacological effects of Myricetin on different diseases such as osteoporotic disorder, anti-inflammatory disorder, alzheimer's disease, anti-epileptic, cancer, cardiac disorder, diabetic metabolic disorder, hepatoprotective disorder and gastro protective disorder. Thieme. All rights reserved.
| Iscriviti per poter valutare questo oggetto, le sue recensioni e per contribuire a Tiiips.ValutaChiudi | (0 commenti) |
Leggi altri Tiiips su questo oggetto in Inglese (1)
Tipologia: Natural Principali sostanze contenute: Ultimo aggiornamento: 2024-09-30 16:27:53 | Rischio chimico: |