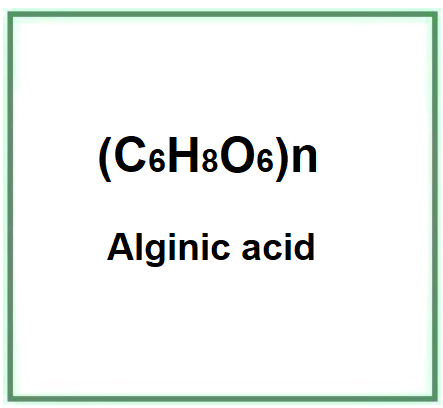
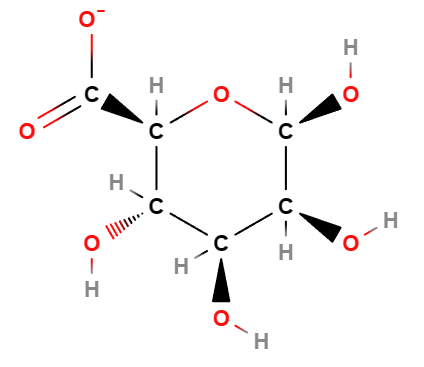
Alginic acid is a complex carbohydrate, linear edible polysaccharide derived from Algin, a natural biodegradable component, a biological polysaccharide and colloidal carbohydrate.
Industrial Production Process
- Harvesting of brown seaweeds. Various types of seaweeds such as Ascophyllum, Laminaria, and Macrocystis are harvested from coastal waters.
- Washing. The harvested seaweeds are washed with seawater to remove salts, sand, and other organic debris.
- Extraction. The washed seaweeds are treated with a solution of sodium bicarbonate to facilitate the release of alginate from the seaweed tissues.
- Precipitation of alginic acid. The alginate in solution is precipitated by adding hydrochloric acid, converting sodium alginate into alginic acid.
- Filtration and washing. The precipitated alginic acid is filtered and washed to remove impurities and excess acid residues.
- Drying. The wet alginic acid is dried at controlled temperatures to obtain a fine powder.
- Quality control. The final product is tested to determine viscosity, purity, and compliance with required standards for its various applications.
It appears in the form of a white powder.

What it is used for and where
Algin is a natural, gelling, soluble polymer found in marine algae and extracted from brown algae such as Turbinaria, Cystoseira, Sargassum, Hormophysa. It is available as propylene glycol alginate, ester, precipitate or paste.
Medical
In medicine, alginic acid is often used as a demulcent agent in antacid preparations for treating conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease, as it can form a protective barrier that prevents stomach acids from irritating the esophagus. Additionally, it is used in dentistry to create dental impressions and in cooking as a thickener and stabilizer in products such as ice cream and sauces.
Food
Algin is added in dairy products, candies, sweets, jellies. It has the number E400 in the list of European food additives as thickener and stabilizer..
Cosmetics
- Binder agent. Ingredient that is used in cosmetic, food and pharmaceutical products as an anti-caking agent with the function of making the product in which it is incorporated silky, compact and homogenous. The binder, either natural such as mucilage, gums and starches or chemical, may be in the form of a powder or liquid.
- Skin conditioning agent. It is the mainstay of topical skin treatment by restoring, increasing or improving skin tolerance to external factors, including melanocyte tolerance. The most important function of the conditioning agent is to prevent skin dehydration, but the subject is rather complex and involves emollients and humectants.
- Surfactant - Suspending agent. Cosmetic or pharmaceutical suspensions are known to be thermodynamically unstable and it is therefore essential to include in the formulation a suspending agent capable of dispersing any sedimented particulates and reducing the rate of sedimentation. The presence of this agent increases the consistency of the suspension medium and exerts a protective colloidal action with a surfactant action.
Other uses
Moisturizing Properties. Alginic acid is an excellent humectant that helps retain moisture on the skin, enhancing hydration and leaving the skin soft and smooth.
Thickening and Gelling Effects. It is used to improve the texture of cosmetic products, giving them a richer and more pleasant touch.
Protective Film Formation. When applied to the skin, it forms a thin film that protects against external irritants and helps maintain hydration.
Antioxidant Properties. Contains antioxidants that help protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals and premature aging.
Use in Peel-off Masks. Particularly popular in peel-off masks, where its ability to form solid gels is utilized to create masks that can be easily removed by pulling, thus helping to cleanse pores and remove impurities.
Skin Compatibility. It is generally well tolerated and can be used on all skin types, including sensitive skin.
It is used in thickening textile paints, paper and textile sizing.
CAS: 9005-32-7
EC number 232-680-1
CAS 9005-32-7
EC number 232-680-1
Bibliografia_____________________________________________________________________
(1) Dağlı Ü, Kalkan İH. Treatment of reflux disease during pregnancy and lactation. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2017 Dec;28(Suppl 1):S53-S56. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2017.14. PMID: 29199169.
Abstract. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is frequently seen during pregnancy. In the medical treatment of pregnant women with GERD, alginic acid and sucralfate can be used. Calcium- and magnesium-based antacids can also be used, particularly for patients with preeclampsia. In particular, ranitidine -a histamine-2 receptor blocker- is preferred. In the case of non-responsiveness to the abovementioned treatments, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), except omeprazole, can be given considering the benefit-harm ratio for the mother and fetus after the first trimester. In cases with GERD during the lactation period, drugs having minimum systemic absorption, such as sucralfate and alginic acid, are preferable but there is no data.
![]() Alginic acid
Alginic acid