Sodium xylenesulfonate: properties, uses, INCI functions, safety
Sodium xylenesulfonate is a sodium chemical compound belonging to a subgroup of the hydrotropic category, dimethyl (xylene sulfonates). It has the characteristic of improving solubility in apolar solvents and reducing solubility in polar solvents such as water.
Sodium Xylenesulfonate is a chemical compound commonly used in cosmetic and personal care products as a solubilizer, surfactant, and viscosity reducer. It helps to enhance the solubility of various ingredients in formulations, making it easier to combine water-soluble and oil-soluble components. It is often found in products like shampoos, body washes, and household cleaners, where it contributes to improved texture and spreadability without affecting the overall effectiveness of the product.
Chemical Composition and Structure
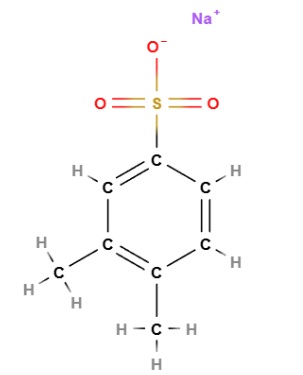
Sodium Xylenesulfonate has the chemical formula C8H9NaO3S, and it is the sodium salt of xylenesulfonic acid. The structure includes a benzene ring with two methyl groups (xylene) attached to a sulfonic acid group, which is then neutralized with sodium. This structure allows it to act as a surfactant and a solubilizing agent, enhancing the mixture of different ingredients in aqueous solutions.
Physical Properties
Sodium Xylenesulfonate is typically a white or pale yellow powder or liquid, depending on its formulation. It is highly soluble in water and is known for its ability to reduce the viscosity of thickened solutions, helping to create smooth, easy-to-apply products. It is also stable across a wide pH range, making it a versatile ingredient in various formulations.
The name defines the structure of the molecule:
- "Sodium" refers to the sodium ion, Na +.
- "Xylene" refers to the aromatic structure of the hydrocarbon ring, which is a six-carbon ring with three double bonds.
- "sulfonate" refers to the sulfonic acid group, -SO3H, which in this case is deprotonated to form a sulfonate ion, -SO3-.
The production of hydrotropics consists in the sulphonation of an aromatic hydrocarbon solvent: toluene, xylene or cumene. Then the resulting aromatic sulfonic acid is neutralized with a specific base such as ammonium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide to obtain the hydrotropic or sulfonate.
The synthesis process takes place in several stages:
- Xylene sulfonation: In the first phase, xylene is reacted with sulfuric acid to form xylensulfonic acid. This reaction typically occurs at high temperatures.
- Neutralization: Xylensulfonic acid is then neutralized with sodium hydroxide to form sodium xylensulfonate. This reaction is exothermic and releases heat.
- Purification: The resulting solution is then purified to remove the unreacted xylene and sulfuric acid. This can be done by several methods, including distillation or crystallization.

What it is used for and where
Cosmetics
Hydrotrope (solubilizing agents). This compound has the property of facilitating the miscibility of other compounds that are poorly soluble in water and does not form micelles in the solubilisation process, even with a chemical reaction of complexation or molecular aggregation. The two fundamental solubilisation factors are the hydrotropic-solute association mediated by the depression of water activity and ionic dissociation.
Health and Safety Considerations
Safety in Use
Sodium Xylenesulfonate is generally considered safe for use in personal care and household products. It has a low risk of causing skin or eye irritation when used at recommended concentrations in rinse-off products. It has been extensively tested and approved by regulatory bodies like the Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR).
Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions to Sodium Xylenesulfonate are rare, but individuals with sensitive skin may experience mild irritation if exposed to high concentrations. Patch testing is recommended for those with a history of sensitivities to surfactants or cleansers.
Toxicity and Carcinogenicity
There is no evidence that Sodium Xylenesulfonate is toxic or carcinogenic. It is considered non-toxic when used as intended in cosmetic and household products, and it does not accumulate in the environment.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Sodium Xylenesulfonate is biodegradable and considered to have a low environmental impact. However, it is important to manage its production and disposal properly to minimize any ecological effects, particularly in aquatic environments.
Regulatory Status
Sodium Xylenesulfonate is approved for use in personal care products in many regions, including the European Union and the United States. It is commonly used in cosmetic and household formulations within regulated concentration limits to ensure consumer safety.
Synonyms:
- Benzenesulfonic acid, dimethyl-, sodium salt
- Dimethylbenzenesulfonic acid, sodium salt
- Sodium dimethylbenzenesulfonate
- Xylenesulfonic acid, sodium salt
- Trade name:Eltesol SX30
- Eltesol SX40
- Eltesol SX93
- Eltesol SX Pellets
- Norfix SXS-40
- Pilot SXS-40
- Stepanate SXS
- Molecular Formula C8H9NaO3S
- Molecular Weight 208.21 g/mol
- CAS 1300-72-7
- UNII 2OYF82G7KK
- EC Number 215-090-9
References__________________________________________________________________________
Horváth-Szabó G, Yin Q, Friberg SE. The Hydrotrope Action of Sodium Xylenesulfonate on the Solubility of Lecithin. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2001 Apr 1;236(1):52-59. doi: 10.1006/jcis.2000.7391.
Saari, R. B., Stansbury, J. S., & Laquer, F. C. (1998). Effect of sodium xylenesulfonate on zinc removal from wastewater. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 124(10), 939-944.
Abstract. Based on new U.S. Environmental Protection Agency rules, many metal finishing and plating facilities have switched, or are evaluating switching, from solvent-based metal cleaning systems to aqueous (or alkaline)-based cleaning systems. Some of the constituents in the aqueous cleaners may inhibit metals removal in wastewater treatment processes. This study was conducted to evaluate the effects of sodium xylenesulfonate (SXS), a constituent of a common aqueous cleaner, on zinc removal from industrial wastewater using hydroxide precipitation. In addition, the effects of polyaluminum chloride (PAC) dosages used in the treatment plant were also evaluated. It was found that low levels of SXS did not significantly affect zinc removal. However, higher concentrations of SXS, especially when combined with greater than optimum levels of PAC, did significantly inhibit zinc removal through hydroxide precipitation.
Friberg, S. E., & Fei, L. (1998). Vapor pressures of phenethyl alcohol and phenethyl acetate in aqueous solutions of sodium xylene sulfonate and polyvinylpyrrolidone. In Horizons 2000–aspects of colloid and interface science at the turn of the millenium (pp. 93-100). Steinkopff.
Abstract. Vapor pressures of two fragrance materials in aqueous solutions of polyvinylpyrrolidone and sodium xylenesulfonate were determined using gas chromatography of head space samples. The association between polymer and hydrotrope was evaluated from the values of surface tension and electrical conductance. The result showed an association of the hydrotrope and the polymer leading to enhanced surface tension after addition of polymer to hydrotope solutions in a certain hydrotope concentration range. The polymer hydrotope association structure resulted in a reduction of fragrance vapor pressure due to solubilization of the fragrance into the association structure.
![]() Sodium xylenesulfonate
Sodium xylenesulfonate