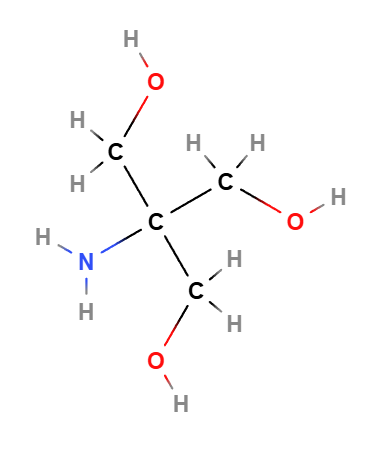
Tromethamine, also known as tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, is a chemical compound commonly used in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals as a pH adjuster and buffering agent. It helps stabilize formulations by maintaining an optimal pH level, ensuring that the product remains effective and gentle on the skin. Tromethamine is often found in a variety of skincare products, including cleansers, creams, and lotions, due to its ability to neutralize acidic components and create a balanced environment for other active ingredients.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Tromethamine has the chemical formula C4H11NO3 and consists of a central amine group (NH2) attached to three hydroxymethyl groups (-CH2OH). This structure allows it to act as a buffer, resisting changes in pH when acids or bases are introduced into a formulation. Its ability to stabilize the pH level makes it an essential ingredient in products where maintaining a consistent pH is crucial for effectiveness and skin compatibility.
Physical Properties
Tromethamine typically appears as a white crystalline powder or granules, but it is also available in aqueous solution form. It is highly soluble in water and has a mild, non-irritating scent. Tromethamine has hygroscopic properties, meaning it can absorb moisture from the air, which further enhances its use in aqueous cosmetic formulations. The compound is stable under normal conditions and works efficiently as a pH buffer across a wide range of temperatures and concentrations.

Production Process
The production of Tromethamine involves the following steps:
Synthesis: Tromethamine is synthetically produced through a chemical reaction between formaldehyde and ammonia, followed by further processing to create the final compound.
Purification: The compound undergoes purification to remove any byproducts or impurities, ensuring high-quality Tromethamine suitable for cosmetic and pharmaceutical use.
Formulation: The purified Tromethamine is then incorporated into cosmetic formulations to serve as a pH adjuster and buffering agent.
Applications
Skincare: Tromethamine is commonly used in a wide range of skincare products such as cleansers, toners, and moisturizers to adjust and maintain the pH balance of the formulation. It ensures that the product is effective without causing irritation, making it suitable for sensitive skin.
Pharmaceuticals: In medical formulations, Tromethamine is often used as a buffering agent in intravenous solutions and medications, helping to maintain the correct pH level for drug stability and patient safety.
Makeup: Tromethamine is also found in makeup formulations, particularly in foundations and powders, where it helps maintain the stability and texture of the product.
Haircare: In shampoos and conditioners, Tromethamine helps regulate the pH to ensure the formula is gentle on the scalp while maintaining product stability.
INCI Functions
Fragrance. It plays a very important role in the formulation of cosmetic products as it allows perfume to be enhanced, masked or added to the final product, improving its commercial viability. The consumer always expects to find a pleasant scent in a cosmetic product.
pH adjuster. This ingredient tends to restore the pH of a cosmetic formulation to its optimal value. The correct pH value is an essential determinant for lipid synthesis in the stratum corneum. The average physiological pH value of the face ranges between 5.67 and 5.76. The hair fibre has a pH value of 3.67.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Tromethamine is generally regarded as safe for use in cosmetic and pharmaceutical products. It is non-irritating and non-sensitizing when used in appropriate concentrations. However, as with any chemical compound, it is essential to follow regulatory guidelines to ensure safe use.
Tromethamine is biodegradable, and its environmental impact is minimal when disposed of properly. It does not bioaccumulate or pose significant risks to aquatic environments.
Molecular Formula C4H11NO3
Molecular Weight 121.14 g/mol
CAS 77-86-1
UNII 023C2WHX2V
EC Number 201-064-4
DTXSID2023723
Synonyms:
- Trometamol
- Tris(Hydroxymethyl)aminomethane
Trade name:
- Pehanorm
- Tham
- Trispuffer
- Trizma
- Talatrol
References__________________________________________________________________________
Becker LC, Bergfeld WF, Belsito DV, Hill RA, Klaassen CD, Liebler DC, Marks JG Jr, Shank RC, Slaga TJ, Snyder PW, Gill LJ, Heldreth B. Safety Assessment of Tromethamine, Aminomethyl Propanediol, and Aminoethyl Propanediol as Used in Cosmetics. Int J Toxicol. 2018 May/Jun;37(1_suppl):5S-18S. doi: 10.1177/1091581817738242.
Abstract. The Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) Expert Panel (Panel) reviewed the safety of tromethamine, aminomethyl propanediol, and aminoethyl propanediolas used in cosmetics. All 3 ingredients are reported to function in cosmetics as pH adjusters, and tromethamine and aminomethyl propanediol are also reported to function as fragrance ingredients. The Panel reviewed relevant animal and human data related to these ingredients, along with a previous safety assessment of aminomethyl propanediol. The Panel concluded that tromethamine, aminomethyl propanediol, and aminoethyl propanediol are safe in cosmetics in the practices of use and concentration as given in this safety assessment.
Nau R, Desel H, Lassek C, Kolenda H, Prange H. Entry of tromethamine into the cerebrospinal fluid of humans after cerebrovascular events. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1999 Jul;66(1):25-32. doi: 10.1016/S0009-9236(99)70050-0.
Abstract. Objective: The intravenous administration of tromethamine (INN, trometamol) lowers the intracranial pressure in patients with brain edema. One postulated mechanism of action is the increase of the pH of the cerebrospinal fluid. Methods: To study tromethamine kinetics in serum and cerebrospinal fluid, nine patients with external ventriculostomies and normal serum creatinine values received 60 mmol intravenous tromethamine (Tris 36.34%, pH 11) over 30 minutes. Serum and cerebrospinal fluid were drawn repeatedly, and concentrations were determined by HPLC.....Conclusion: Tromethamine cerebrospinal fluid concentrations will be high enough to increase the pH of the cerebrospinal fluid only at large doses and in patients with a pronounced disruption of the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier.
![]() Tromethamine
Tromethamine