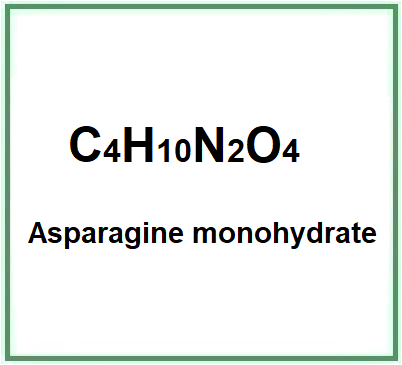
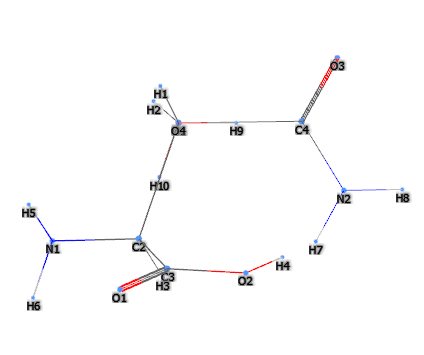
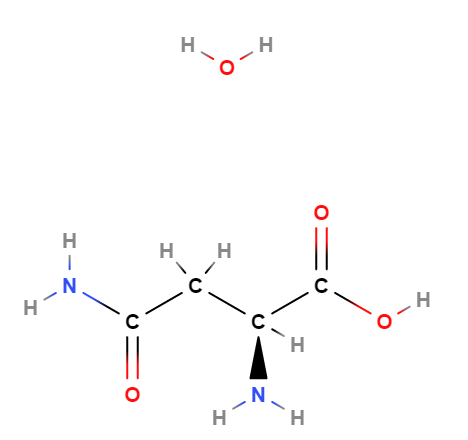
Compendium of the most significant studies with reference to properties, intake, effects.
Lenka, M., & Sarkar, D. (2016). Solubility of l-asparagine monohydrate in water and water-isopropanol mixed solvents: measurements and thermodynamic modelling. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 412, 168-176.
Abstract. The solubility of l-asparagine monohydrate (LAM) in pure water and various water-isopropanol mixtures is determined in the temperature range from 298.15 K to 333.15 K using gravimetric method. The solubility of LAM increases with increasing temperature at a given solvent composition within the temperature range studied, and decreases with increasing isopropyl alcohol(IPA) ratio over the same temperature range for water-IPA mixture. The NRTL and UNIQUAC framework with adjustable binary parameters were used to correlate the experimental solubility data and the computed solubilities are in good agreement with experimental observations. The heat of fusion for LAM was considered as an additional parameter for both the models and was estimated along with binary parameters using experimental solubility data and a nonlinear regression method. The dissolution enthalpy and dissolution entropy of the solution of LAM in pure water and water-IPA mixtures were also obtained using van't Hoff equation.
Görbitz CH, Hartviksen LM. The monohydrates of the four polar dipeptides L-seryl-L-asparagine, L-seryl-L-tyrosine, L-tryptophanyl-L-serine and L-tyrosyl-L-tryptophan. Acta Crystallogr C. 2008 Mar;64(Pt 3):o171-6. doi: 10.1107/S0108270108004228.
Abstract. The crystal structures of the four dipeptides L-seryl-L-asparagine monohydrate, C(7)H(13)N(3)O(5) x H(2)O, L-seryl-L-tyrosine monohydrate, C(12)H(16)N(2)O(5) x H(2)O, L-tryptophanyl-L-serine monohydrate, C(14)H(17)N(3)O(4) x H(2)O, and L-tyrosyl-L-tryptophan monohydrate, C(20)H(21)N(3)O(4) x H(2)O, are dominated by extensive hydrogen-bonding networks that include cocrystallized solvent water molecules. Side-chain conformations are discussed on the basis of previous observations in dipeptides. These four dipeptide structures greatly expand our knowledge on dipeptides incorporating polar residues such as serine, asparagine, threonine, tyrosine and tryptophan.
de Moraes LS, Kennedy AR, Logan CR. Crystal structures of three halide salts of l-asparagine: an isostructural series. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2018 Oct 19;74(Pt 11):1619-1623. doi: 10.1107/S2056989018014603.
Abstract: The structures of three monohydrated halide salt forms of l-asparagine are presented, viz. l-asparaginium chloride monohydrate, C4H9N2O3 +·Cl-·H2O, (I), l-asparaginium bromide monohydrate, C4H9N2O3 +·Br-·H2O, (II), and l-asparaginium iodide monohydrate, C4H9N2O3 +·I-·H2O, (III). These form an isomorphous and isostructural series. The C-C-C-C backbone of the amino acid adopts a gauche conformation in each case [torsion angles for (I), (II) and (III) = -55.4 (2), -55.6 (5) and -58.3 (7)°, respectively]. Each cation features an intra-molecular N-H⋯O hydrogen bond, which closes an S(6) ring. The extended structures feature chains of cations that propagate parallel to the b-axis direction. These are formed by carb-oxy-lic acid/amide complimentary O-H⋯O + N-H⋯O hydrogen bonds, which generate R 2 2(8) loops. These chains are linked by further hydrogen bonds mediated by the halide ions and water mol-ecules to give a layered structure with cation and anion layers parallel to the ab plane. Compound (III) was refined as an inversion twin.
Yamada, K., Hashizume, D., Shimizu, T., & Yokoyama, S. (2007). l-Asparagine. Acta Crystallographica Section E: Structure Reports Online, 63(9), o3802-o3803.
Abstract. Crystals of anhydrous L-aspargine, C4H8N2O3, were obtained from a saturated aqueous solution. The molecules are in their zwitterionic form. Although the carboxyl group is deprotonated, the distances of the two C[pdbond]O bonds are significantly different [1.2407 (19) and 1.262 (2) Å], due to different hydrogen-bond environments. The conformation of the side chain is trans, which distinguishes it significantly from that of L-asparagine monohydrate.
![]() Asparagine monohydrate
Asparagine monohydrate