Hexyldecanol: : properties, uses, pros, cons, safety
Hexyldecanol is a chemical compound, aliphatic alcohol.
The name defines the structure of the molecule
- "Hexyl". Indicates the presence of a hexyl side chain, which is an alkyl group.
- "Decanol". Is a fatty alcohol with a chain of 10 carbon atoms.
Description of the raw materials used in its production.
- Fatty Aldehyde - For example, decanal, an aldehyde with a 10-carbon chain.
- Fatty Alcohol - For example, hexan-1-ol, an alcohol with a 6-carbon chain.
- Catalyst - For example, potassium hydroxide or sulfuric acid, used to catalyze the reaction.
Step-by-step summary of its industrial chemical synthesis process.
- Preparation of Reagents - Decanal and hexan-1-ol are prepared or purchased as raw materials.
- Chain Extension Reaction - The fatty aldehyde (decanal) reacts with the fatty alcohol (hexan-1-ol) in the presence of a catalyst. This extends the carbon chain of the aldehyde.
- Reduction - The product formed in step 2 is reduced to an alcohol, which in this case is Hexyldecanol.
- Purification - The product is purified to remove impurities and unreacted reagents, e.g., by distillation.
It occurs as a red/amber liquid.

What it is used for and where
Raw material for the production of surfactants, perfumes, herbicides, plasticisers, synthetic fibres, defoamers, lubricant additives, etc..
Food
- Used in small quantities in the preparation of various fruit, cream, coconut etc. flavours.
- Ripening agent for green fruits
Cosmetics
Dispersant and, in small amounts, incorporated into fragrances in scented soaps and as a mixing agent for linalool.
Skin conditioning agent. It is the mainstay of topical skin treatment as it has the function of restoring, increasing or improving skin tolerance to external factors, including melanocyte tolerance. The most important function of the conditioning agent is to prevent skin dehydration, but the subject is rather complex and involves emollients and humectants that can be added in the formulation.
Skin conditioning agent - Emollient. Emollients have the characteristic of enhancing the skin barrier through a source of exogenous lipids that adhere to the skin, improving barrier properties by filling gaps in intercorneocyte clusters to improve hydration while protecting against inflammation. In practice, they have the ability to create a barrier that prevents transepidermal water loss. Emollients are described as degreasing or refreshing additives that improve the lipid content of the upper layers of the skin by preventing degreasing and drying of the skin. The problem with emollients is that many have a strong lipophilic character and are identified as occlusive ingredients; they are oily and fatty materials that remain on the skin surface and reduce transepidermal water loss. In cosmetics, emollients and moisturisers are often considered synonymous with humectants and occlusives.
Printing Industry
Industry
- Industrial deodorisation. To cover bad odours of industrial products.
PVC
- Raw material for PVC yarn coating materials and plasticisers
Other applications
- Solvent and stabiliser for synthetic raw materials, pesticides, herbicides.
- Oil drilling and in secondary oil recovery.
Safety
Chemical compound generally considered safe for human health. Sporadic episodes of specific allergy may occur, as with any chemical compound.
Hexyldecanol studies
Typical optimal commercial product characteristics 2-hexyldecan-1-ol
| Appearance | Amber liquid |
| Boiling Point | 304.4±10.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | -21--15ºC |
Flash Point
| 118.6±7.1°C |
| Acid value | 0.1Max |
Saponification value
| 0.5Max |
| Hydroncarbons Wt% | 1Max |
| Hydroxyl mg KOH/g | 351-357 |
| Iodine g/100g | 0.3Max |
| PSA | 20.23000 |
| LogP | 7.07 |
Index of Refraction
| 1,447 |
Vapour Pressure
| 0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C |
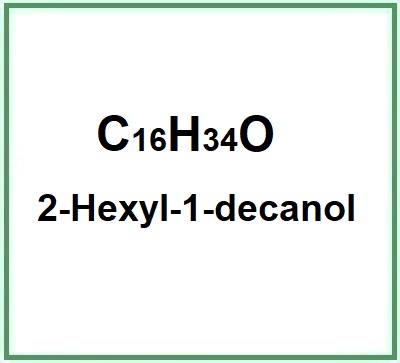
- Molecular Formula C16H34O C10H22O
- Linear Formula CH3(CH2)7CH[(CH2)5CH3]CH2OH
- Molecular Weight 242.44
- Exact Mass 242.260971
- CAS 2425-77-6 112-30-1
- UNII 151Z7P1317
- EC Number 219-370-1 203-956-9
- DSSTox Substance ID DTXSID1041265
- IUPAC 2-hexyldecan-1-ol
- InChI=1S/C16H34O/c1-3-5-7-9-10-12-14-16(15-17)13-11-8-6-4-2/h16-17H,3-15H2,1-2H3
- InChl Key XULHFMYCBKQGEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
- SMILES CCCCCCCCC(CCCCCC)CO
- MDL number MFCD00060903
- PubChem Substance ID 24870185
- ChEBI 183266
- NSC 2399
Synonyms:
- 2-Hexyl-1-decanol
- 1-Decanol, 2-hexyl-
- 2-Hexyldecanol
References__________________________________________________________________________
Bährle-Rapp, M. (2007). Hexyldecanol. In Springer Lexikon Kosmetik und Körperpflege (pp. 256-256). Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Hakozaki, T., Laughlin, T., Zhao, S., Wang, J., Deng, D., Jewell‐Motz, E., & Elstun, L. (2013). A regulator of ubiquitin–proteasome activity, 2‐hexyldecanol, suppresses melanin synthesis and the appearance of facial hyperpigmented spots. British Journal of Dermatology, 169, 39-44.
Abstract. Background. 2-Hexyldecanol has long been used in skin-care products, but has not previously been reported as an active ingredient for skin benefits. Objectives. To evaluate 2-hexyldecanol in in vitro and ex vivo systems and, if found to be active, progress it to topical clinical testing to determine effects on pigmentation in skin. Methods. 2-Hexyldecanol was tested in melanocyte cell culture systems (B16 mouse melanoma cells and normal human melanocytes) for its effect on proteolytic activity and melanin production, in the absence and presence of the proteasome-specific inhibitor, MG132. It was further tested in a human skin explant model for its effect on melanin production. Lastly, topically applied 2-hexyldecanol was evaluated for its effect on the appearance of facial pigmentation in an 8-week, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled, split-face incomplete block design study in Chinese women. Results. In submerged cell culture, 2-hexyldecanol upregulated proteolytic activity and decreased melanin synthesis. These effects were antagonized by the proteasome-specific inhibitor MG132. MG132, tested in the absence of 2-hexyldecanol, increased melanin production. In a human skin explant model, topical 2-hexyldecanol suppressed the production of melanin vs. a vehicle control. In a human clinical study in Chinese women (n = 110 observations per test material), a 2-hexyldecanol-containing formulation significantly reduced the appearance of facial hyperpigmented spots vs. its control. Conclusions. These data indicate that regulation of proteasome activity is a viable target for control of melanin production, that 2-hexyldecanol upregulates proteasomal activity in melanocytes, and that topical 2-hexyldecanol reduces the appearance of hyperpigmentation.
![]() Hexyldecanol
Hexyldecanol