![]() Condroitina solfato
Condroitina solfato
Media gradimento : 7.5
| Valutazione | N. Esperti | Valutazione | N. Esperti |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | ||
| 2 | 7 | ||
| 3 | 8 | ||
| 4 | 9 | ||
| 5 | 10 |
18 pt da CarPas
| Iscriviti per poter valutare questo oggetto, le sue recensioni e per contribuire a Tiiips.Valuta | Dove si trova? |
| "Chondroitin solfato studi" su Condroitina solfato Consenso relazione 9 di A_Partyns (13046 pt) | 05-set-2021 16:27 |
| Leggi il Tiiip completo | (Invia il tuo commento) |
Compendio degli studi più significativi con riferimento a proprietà, assunzione, effetti.
Mukherjee N, Nandi S, Garg S, Ghosh S, Ghosh S, Samat R, Ghosh S. Targeting Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycans: An Emerging Therapeutic Strategy to Treat CNS Injury. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020 Feb 5;11(3):231-232. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00004.
Abstract
Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans (CSPGs) are the most abundant components of glial scar formed after severe traumatic brain injury as well as spinal cord injury and play a crucial inhibitory role in axonal regeneration by selective contraction of filopodia of the growth cone of sprouting neurites. Healing of central nervous system (CNS) injury requires degradation of the glycosamine glycan backbone of CSPGs in order to reduce the inhibitory effect of the CSPG layer. The key focus of this Viewpoint is to address a few important regenerative approaches useful for overcoming the inhibitory barrier caused by chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans.
Stephenson EL, Yong VW. Pro-inflammatory roles of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans in disorders of the central nervous system. Matrix Biol. 2018 Oct;71-72:432-442. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2018.04.010.
Abstract
The extracellular matrix of the central nervous system is an interconnected network of proteins and sugars. It is crucial for homeostasis, but its remodeling in neurological diseases impacts both injury and repair. Here we introduce an extracellular matrix family member that participates in immune-matrix interactions, the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans. Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans integrate signals from the microenvironment to activate immune cells, and they boost inflammatory responses by binding immunological receptors including toll-like receptors, selectins, CD44, and β1 integrin. Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans also bind signaling molecules for immune cells such as cytokines and chemokines, and they activate matrix-degrading enzymes. Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans accumulate in the damaged CNS, including during traumatic brain/spinal cord injury and multiple sclerosis, and they help drive pathogenesis. This Review aims to give new insights into the remodeling of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans during inflammation, and how these matrix glycoproteins are able to drive neuroinflammation.
Stephenson EL, Mishra MK, Moussienko D, Laflamme N, Rivest S, Ling CC, Yong VW. Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans as novel drivers of leucocyte infiltration in multiple sclerosis. Brain. 2018 Apr 1;141(4):1094-1110. doi: 10.1093/brain/awy033.
Abstract
Multiple sclerosis presents with profound changes in the network of molecules involved in maintaining central nervous system architecture, the extracellular matrix. The extracellular matrix components, particularly the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans, have functions beyond structural support including their potential interaction with, and regulation of, inflammatory molecules. To investigate the roles of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans in multiple sclerosis, we used the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model in a time course study. We found that the 4-sulfated glycosaminoglycan side chains of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans, and the core protein of a particular family member, versican V1, were upregulated in the spinal cord of mice at peak clinical severity, correspondent with areas of inflammation. Versican V1 expression in the spinal cord rose progressively over the course of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. A particular structure in the spinal cord and cerebellum that presented with intense upregulation of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans is the leucocyte-containing perivascular cuff, an important portal of entry of immune cells into the central nervous system parenchyma. In these inflammatory perivascular cuffs, versican V1 and the glycosaminoglycan side chains of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans were observed by immunohistochemistry within and in proximity to lymphocytes and macrophages as they migrated across the basement membrane into the central nervous system. Expression of versican V1 transcript was also documented in infiltrating CD45+ leucocytes and F4/80+ macrophages by in situ hybridization. To test the hypothesis that the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans regulate leucocyte mobility, we used macrophages in tissue culture studies. Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans significantly upregulated pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in macrophages. Strikingly, and more potently than the toll-like receptor-4 ligand lipopolysaccharide, chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans increased the levels of several members of the matrix metalloproteinase family, which are implicated in the capacity of leucocytes to cross barriers. In support, the migratory capacity of macrophages in vitro in a Boyden chamber transwell assay was enhanced by chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans. Finally, using brain specimens from four subjects with multiple sclerosis with active lesions, we found chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans to be associated with leucocytes in inflammatory perivascular cuffs in all four patients. We conclude that the accumulation of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans in the perivascular cuff in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis boosts the activity and migration of leucocytes across the glia limitans into the central nervous system parenchyma. Thus, chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans represent a new class of molecules to overcome in order to reduce the inflammatory cascades and clinical severity of multiple sclerosis.
Ishibashi K, Iwai H, Koga H. Chemonucleolysis with chondroitin sulfate ABC endolyase as a novel minimally invasive treatment for patients with lumbar intervertebral disc herniation. J Spine Surg. 2019 Jun;5(Suppl 1):S115-S121. doi: 10.21037/jss.2019.04.24.
Abstract
Chemonucleolysis is a minimally invasive treatment for cervical and lumbar intervertebral disc herniation (IDH). While this procedure has existed for more than 50 years, it has yet to become an established practice. The main reason for this is the low specificity of enzymes targeting nucleus pulposus (NP). Although two enzymes (chymopapain and collagenase) have been used in clinical settings, severe adverse events have discouraged widespread use. The recently introduced enzyme Proteus vulgaris chondroitin sulfate ABC endolyase may allow a new era of chemonucleolysis because of its high specificity for NP.
Sugahara K, Mikami T. Chondroitin/dermatan sulfate in the central nervous system. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2007 Oct;17(5):536-45. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2007.08.015.
Abstract
In the central nervous system (CNS) chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans, as one of the major barrier-forming molecules, influence cell migration patterns and axon pathfinding. By contrast, chondroitin sulfate side chains often form hybrid chains with dermatan sulfate and serve as a neural stem cell marker and neurogenic/neuritogenic molecules involved in neural stem cell proliferation. Hybrid chondroitin/dermatan sulfate chains are also involved in formation of the neural network by capturing and presenting heparin-binding growth factors like basic fibroblast growth factor, pleiotrophin, and hepatocyte growth factor to stem cells or neuronal cells. Research tools for structural glycobiology are emerging to perform a high-throughput screening of glycosaminoglycans for the binding to ligands, to decipher sulfation patterns of rare functional oligosaccharide sequences and to build structural models for the shape of such sulfated oligosaccharides.
Volpi N. Quality of different chondroitin sulfate preparations in relation to their therapeutic activity. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2009 Oct;61(10):1271-80. doi: 10.1211/jpp/61.10.0002.
Aono S, Oohira A. Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans in the brain. Adv Pharmacol. 2006;53:323-36. doi: 10.1016/S1054-3589(05)53015-1
Yang X. Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans: key modulators of neuronal plasticity, long-term memory, neurodegenerative, and psychiatric disorders. Rev Neurosci. 2020 Jul 28;31(5):555-568. doi: 10.1515/revneuro-2019-0117.
Asai A, Hatayama N, Kamiya K, Yamauchi M, Kinashi H, Yamaguchi M, Katsuno T, Nobata H, Watanabe K, Wakatsuki A, Aten J, Maruyama S, Ishimoto T, Hirai S, Naito M, Ito Y. Roles of glomerular endothelial hyaluronan in the development of proteinuria. Physiol Rep. 2021 Sep;9(17):e15019. doi: 10.14814/phy2.15019.
| Iscriviti per poter valutare questo oggetto, le sue recensioni e per contribuire a Tiiips.ValutaChiudi | (0 commenti) |
| "Descrizione" su Condroitina solfato Consenso relazione 18 di CarPas (5226 pt) | 05-set-2021 17:31 |
| Leggi il Tiiip completo | (Invia il tuo commento) |
I glicosamminoglicani sono i componenti più importanti nella matrice di molecole dei tessuti connettivi dei vertebrati.
Nella funzionalità delle proteine, condroitina solfato, il secondo gruppo più presente e più eterogeneo dopo eparan solfato tra i glicosamminoglicani (polisaccaridi anionici lineari), svolge un ruolo fondamentale tra i componenti della glicosilazione.
Questo studio ha esplorato gli effetti di condroitina solfato sull'osteoartrosi del ginocchio in uno studio di confronto della dose di un anno, randomizzato, in doppio cieco. Nel sottogruppo con sintomi gravi (indice di Lequesne ≥8), la dose di condroitina solfato di 1560 mg/die ha migliorato il dolore più velocemente dopo 6 e 9 mesi di terapia. Tuttavia, non sono stati riscontrati effetti dose-correlati sulla proteina della matrice oligomerica della cartilagine o sui livelli di acido ialuronico (1).
Questa revisione valuta gli studi pubblicati sull'effetto dei sali di glucosamina e dei preparati di condroitina solfato sulla progressione dell'osteoartrite del ginocchio o dell'anca. Diversi potenziali fattori confondenti, tra cui la risposta al placebo, l'uso di farmaci da prescrizione rispetto a pillole da banco o integratori alimentari, o l'uso di glucosamina solfato contro glucosamina cloridrato, possono avere rilevanza quando si tenta di interpretare i risultati apparentemente contraddittori di diversi studi clinici. Sulla base dei risultati di recenti studi randomizzati controllati e meta-analisi, possiamo concludere che il glucosamina solfato (ma non la glucosamina cloridrato) e il condroitina solfato hanno un'efficacia sintomatica da piccola a moderata nell'osteoartrite, sebbene questo sia ancora dibattuto. Per quanto riguarda l'effetto modificante la struttura, ci sono prove convincenti che il solfato di glucosamina e il condroitina solfato possono interferire con la progressione dell'osteoartrite (2).
Condroitina solfato ha numerosi ruoli nella stabilizzazione della matrice e nella regolazione cellulare e specifici ruoli regolatori cellulari che controllano la funzione tissutale e l'omeostasi. Studi sul moscerino della frutta, Drosophila melanogaster e il nematode Caenorhabditis elegans hanno fornito informazioni approfondite sull'interconnettività neurale e sul ruolo dell'ECM e dei suoi PG nello sviluppo neurale e nella morfogenesi tissutale in un ambiente di intero organismo (3)
Gli effetti farmacologici descritti in questo studio indicano che Condroitina solfato è una potenziale molecola per ulteriori studi sulla relazione tra le strutture e le funzioni dei solfati di condroitina come antiossidanti (4).
Uno studio su pazienti di età compresa tra 40 e 99 anni ha verificato l'ipotesi che l'uso di condroitina solfato possa ridurre il rischio di infarto miocardico acuto. Sono stati inclusi un totale di 23.585 casi di incidenti di infarto miocardico acuto e 117.405 controlli. I risultati supportano un effetto cardioprotettivo di Condroitina solfato, mentre la glucosamina sembra essere neutra. La protezione era notevole tra i sottogruppi ad alto rischio cardiovascolare (5).
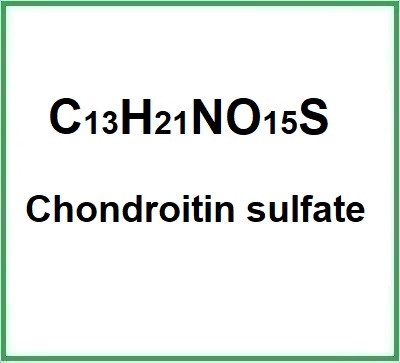
Formula molecolare: C13H21NO15S
Peso molecolare: 463.37 g/mol
CAS: 9007-28-7 9082-07-9 25322-46-7 39455-18-0
UNII
EC Number: 232-696-9 246-844-5 609-686-1 618-658-8
DSSTox Substance ID: DTXSID8031021
NACRES: NA.24
Sinonimi:
- Chondroitin sulfate sodium salt
- Chondroitin sulfate C
- Chondroitin sulfuric acid
Bibliografia__________________________________________________________________
(1) Morita M, Yamada K, Date H, Hayakawa K, Sakurai H, Yamada H. Efficacy of Chondroitin Sulfate for Painful Knee Osteoarthritis: A One-Year, Randomized, Double-Blind, Multicenter Clinical Study in Japan. Biol Pharm Bull. 2018 Feb 1;41(2):163-171. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b17-00556.
(2) Bruyere O, Reginster JY. Glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate as therapeutic agents for knee and hip osteoarthritis. Drugs Aging. 2007;24(7):573-80. doi: 10.2165/00002512-200724070-00005.
(3) Hayes AJ, Melrose J. Neural Tissue Homeostasis and Repair Is Regulated via CS and DS Proteoglycan Motifs. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 2;9:696640. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.696640.
(4) Medeiros LHC, Vasconcelos BMF, Silva MB, Souza-Junior AA, Chavante SF, Andrade GPV. Chondroitin sulfate from fish waste exhibits strong intracellular antioxidant potential. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2021 Jul 16;54(10):e10730. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2020e10730.
(5) Mazzucchelli R, Rodríguez-Martín S, García-Vadillo A, Gil M, Rodríguez-Miguel A, Barreira-Hernández D, García-Lledó A, de Abajo FJ. Risk of acute myocardial infarction among new users of chondroitin sulfate: A nested case-control study. PLoS One. 2021 Jul 12;16(7):e0253932. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0253932.
| Iscriviti per poter valutare questo oggetto, le sue recensioni e per contribuire a Tiiips.ValutaChiudi | (0 commenti) |
Leggi altri Tiiips su questo oggetto in Inglese (2)
Tipologia: Natural Principali sostanze contenute: Ultimo aggiornamento: 2021-09-05 16:38:45 | Rischio chimico: |