![]() CALCITONIN CT
CALCITONIN CT
Rating : 9
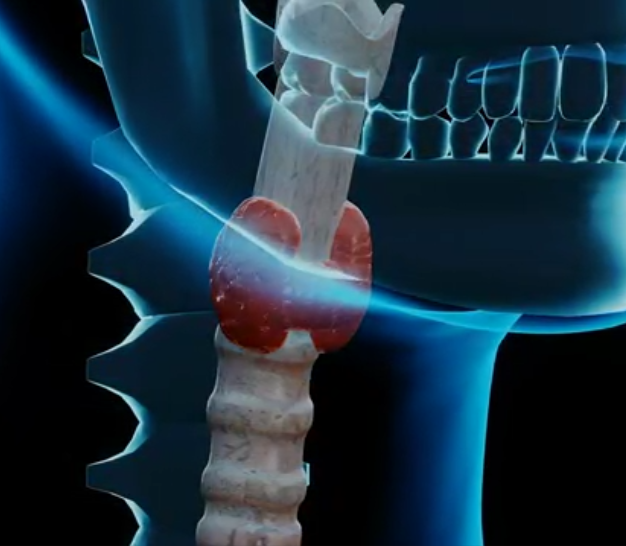
Calcitonin, also called thyrocalcitonin because it is produced by the C cells of the thyroid, which are not part of the follicle wall and pour calcitonin into the capillaries, is another regulatory hormone of calcium metabolism.Calcitonin is also a peptide and is synthesized in the form of prepro-calcitonin, it has opposite effects to those of para... (Read the full Tiiip)
8 pts from Al222
| Evaluate | Where is this found? |
| "Descrizione" about CALCITONIN CT Review Consensus 8 by Al222 (23438 pt) | 2021-Apr-24 12:22 |
Calcitonin, also called thyrocalcitonin because it is produced by the C cells of the thyroid, which are not part of the follicle wall and pour calcitonin into the capillaries, is another regulatory ho ...
| Read the full Tiiip | (Send your comment) |
Read other Tiiips about this object in __Italiano (1)
Component type: Natural Main substances: Last update: 2021-04-24 12:11:37 | Chemical Risk: |