| "Descrizione" by Al222 (24812 pt) | 2025-Jul-26 17:09 |
Definition
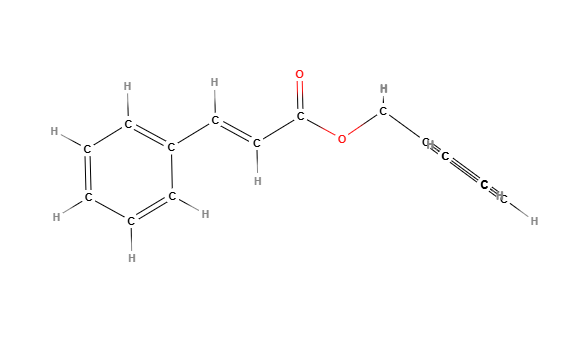
Benzyl cinnamate is an aromatic ester compound formed by the esterification of cinnamic acid and benzyl alcohol. It has a sweet, balsamic, and vanilla-like fragrance and is used in perfumery, cosmetics, and occasionally in pharmaceutical products. In nature, it is found in certain plant resins, particularly Peru balsam and Tolu balsam.
1. Chemical structure
IUPAC name: benzyl (2E)-3-phenylprop-2-enoate
Molecular formula: C₁₆H₁₄O₂
Molar mass: 238.28 g/mol
Appearance: viscous liquid or crystalline solid at room temperature
Color: colorless to pale yellow
Odor: sweet, balsamic, slightly spicy
Solubility: insoluble in water, soluble in ethanol, oils, and organic solvents
2. Natural occurrence
Naturally present in small amounts in:
Peru balsam
Tolu balsam
Some other tropical resins and essential oils
Commercial form is mostly synthetic, produced through esterification.
3. Main associated compounds (in natural sources)
While benzyl cinnamate is a pure substance, in natural balsams it may be accompanied by:
Cinnamyl cinnamate
Benzyl benzoate
Vanillin
Benzoic acid
Essential oil terpenes and resins
4. Method of synthesis or production
Industrial synthesis typically involves:
Reactants: cinnamic acid + benzyl alcohol
Reaction: acid-catalyzed esterification, often using sulfuric acid or p-toluenesulfonic acid
Conditions: reflux and continuous removal of water
Purification: via fractional distillation or crystallization
The result is a stable, odor-rich ester suitable for fragrance applications.
5. Cosmetic and functional properties
Fragrance: used as a base note in perfumes (warm, sweet, ambery)
Fixative: slows down the evaporation of more volatile fragrance components
Emollient: adds smooth texture to skincare products
Solubilizer: helps dissolve fragrance oils and essential oils in emulsions
6. Applications
Cosmetics and perfumery
Perfumes and eau de toilette (especially oriental, sweet, or floral accords)
Creams and lotions
Hair care products
Soaps and scented body cleansers
INCI Functions:
Perfuming. Unlike fragrance, which can also contain slightly less pleasant or characteristic odours, the term perfume indicates only very pleasant fragrances. Used for perfumes and aromatic raw materials.
Cosmetic Safety
Restricted cosmetic ingredient as III/81 a Relevant Item in the Annexes of the European Cosmetics Regulation (EU) 2023/1545. Substance or ingredient reported: 2-Propenoic acid, 3-phenyl-, phenylmethyl ester. The presence of the substance must be indicated in the list of ingredients referred to in Article 19(1)g when its concentration exceeds: - 0.001% in leave-on products - 0.01% in rinse-off products
Pharmaceuticals
Minor component in some topical ointments due to mild antimicrobial or soothing effects
Food (limited use)
May be used as a flavoring agent in trace amounts, depending on country regulations
7. Safety and regulations
Potential allergen: can cause skin sensitization in individuals allergic to balsams or fragrance ingredients
EU Cosmetics Regulation (EC) No. 1223/2009 – Annex III:
Listed among the 26 fragrance allergens
Must be declared on cosmetic labels if present above:
0.001% in leave-on products
0.01% in rinse-off products
Not classified as mutagenic, carcinogenic, or reprotoxic
IFRA (International Fragrance Association): allows its use with concentration limits depending on the product category
8. Conclusion
Benzyl cinnamate is a stable, aromatic ester valued for its sweet and warm fragrance profile. It is primarily used in perfumes and scented cosmetics, where it serves both as a fragrance compound and a fixative. Though generally safe, it is a regulated allergen, and care should be taken when used in products intended for sensitive skin or allergenic individuals.
 |  |
Comparison: Benzyl cinnamate vs Cinnamal vs Benzyl benzoate
| Property | Benzyl cinnamate | Cinnamal (Cinnamaldehyde) | Benzyl benzoate |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAS number | 103-41-3 | 104-55-2 | 120-51-4 |
| Chemical class | Aromatic ester | Aromatic aldehyde | Aromatic ester |
| Molecular formula | C₁₆H₁₄O₂ | C₉H₈O | C₁₄H₁₂O₂ |
| Odor profile | Sweet, balsamic, vanilla-like | Spicy, warm, cinnamon-like | Mild, balsamic, floral, slightly sweet |
| Source | Synthetic or natural (Peru/Tolu balsam) | Natural (cinnamon bark oil) or synthetic | Natural (Peru balsam) or synthetic |
| Main use | Fragrance, fixative, emollient | Fragrance, flavoring agent | Solvent, fixative, fragrance carrier |
| IFRA status | Restricted (sensitizer) | Restricted (strong sensitizer) | Restricted (low to moderate sensitizer) |
| EU label requirement | Yes (Annex III allergen) | Yes (Annex III allergen) | Yes (Annex III allergen) |
| Leave-on threshold | 0.001% | 0.001% | 0.001% |
| Rinse-off threshold | 0.01% | 0.01% | 0.01% |
| Additional risks | Allergenicity | Potent skin sensitizer, eye irritant | Low acute toxicity; can cause allergic reactions |
| Other uses | Flavoring (limited) | Common food flavoring (regulated levels) | Used in topical medications and insect repellents |
Overview of IFRA-restricted fragrance allergens and EU labeling
1. EU Cosmetics Regulation 1223/2009 – Annex III (Labeling of allergens)
Currently, 26 fragrance allergens must be declared on cosmetic labels if present above:
0.001% in leave-on products
0.01% in rinse-off products
Examples include:
Hydroxycitronellal
Cinnamal
Benzyl alcohol
Benzyl benzoate
Benzyl cinnamate
Citral
Limonene
Eugenol
Linalool
Geraniol
Isoeugenol
2. IFRA (International Fragrance Association) Standards
IFRA defines safe usage concentrations for each compound, depending on product type, such as:
Leave-on (face cream, perfume, deodorant)
Rinse-off (shampoo, body wash)
Products with mucosal contact (lip balm, toothpaste)
Substances are classified as:
Prohibited (e.g., Lyral, Lilial)
Restricted (e.g., benzyl cinnamate, cinnamal, benzyl benzoate)
Unrestricted (only if no risk is identified)
Compliance with IFRA is voluntary but considered best practice in the fragrance industry.
Benzyl cinnamate, cinnamal, and benzyl benzoate are widely used aromatic ingredients with allergenic potential.
All three are regulated by EU law and restricted under IFRA standards.
Proper labeling and formulation limits are key to maintaining consumer safety.
Brands that comply with IFRA + EU regulations demonstrate a higher commitment to transparency and dermatological safety.
References__________________________________________________________________________
Thiyagarajan V, Lee KW, Leong MK, Weng CF. Potential natural mTOR inhibitors screened by in silico approach and suppress hepatic stellate cells activation. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2018 Dec;36(16):4220-4234. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2017.1411295.
Abstract. The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), an atypical serine/threonine kinase, plays a central role in the regulation of cell proliferation, growth, differentiation, migration, and survival. In this study, the 3-D structure of the mTOR (PDB ID: 2FAP) was used for the docking of 47 natural compounds and compared with pharmacophore model of 14 known mTOR inhibitors to identify the novel and specific natural inhibitor. The top four compounds, rutin, curcumin, antroquinonol, and benzyl cinnamate, have been selected based on their PLP score and further validated with hepatic stellate cells NHSC and THSC. Curcumin and antroquinonol significantly inhibited NHSC and THSC cells proliferation in a dose-dependent manner, whereas rutin and benzyl cinnamate showed less alteration of cell viability. Rutin inhibited the phosphorylation of mTOR (p-mTOR) and p-p70 S6 K in NHSC and THSC cells by Western blotting. Additionally, p-p70 S6 K protein was significantly decreased by incubation with benzyl cinnamate and curcumin in THSC cells. Taken together, this result suggests that rutin is a potential mTOR inhibitor in screen hits of molecular docking to hamper the activation of HSC and further applications in the treatment of liver fibrosis.
Ohkawara S, Tanaka-Kagawa T, Furukawa Y, Nishimura T, Jinno H. Activation of the human transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 1 by essential oils. Biol Pharm Bull. 2010;33(8):1434-7. doi: 10.1248/bpb.33.1434.
Abstract. Transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 1 (TRPV1) is a non-selective cation channel activated by capsaicin. TRPV1 is expressed not only on human sensory neurons but also on human epidermal and hair follicle keratinocytes. Therefore, TRPV1 could have the potential to be a therapeutic target for skin disorders. To search for novel TRPV1 agonists, we screened 31 essential oils by using human TRPV1-expressing HEK293 cells. TRPV1 was activated by 4 essential oils: rose, thyme geraniol, palmarosa, and tolu balsam. The dose-response curves for TRPV1 activation by the essential oils revealed a rank order potency [the half-maximal effective concentration (EC(50))] of rose>palmarosa>thyme geraniol>tolu balsam, and rank order efficiency (% activity in response to 1 microM capsaicin) of tolu balsam>rose>palmarosa>thyme geraniol. Moreover, the dose-response curves for TRPV1 activation by citronellol (main constituent of rose oil) and geraniol (main constituent of thyme geraniol and palmarosa oils) were consistent with the potency and efficiency of each essential oil. In contrast, benzyl cinnamate and benzyl benzoate (main constituent of tolu balsam oil) and geranyl acetate (main constituent of thyme geraniol oil) did not show TRPV1 activity. In this first-of-its-kind study, we successfully investigated the role of some essential oils in promoting human TRPV1 activation, and also identified two monoterpenes, citronellol and geraniol, as new human TRPV1 agonists.
EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP); Bampidis V, Azimonti G, Bastos ML, Christensen H, Dusemund B, Fašmon Durjava M, Kouba M, López-Alonso M, López Puente S, Marcon F, Mayo B, Pechová A, Petkova M, Ramos F, Sanz Y, Villa RE, Woutersen R, Galobart J, Manini P. Safety of 37 feed additives consisting of flavouring compounds belonging to different chemical groups for use in all animal species (FEFANA asbl). EFSA J. 2022 Apr 19;20(4):e07249. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2022.7249.
Abstract. Following a request from the European Commission, the EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP) was asked to deliver a scientific opinion on the supplementary information submitted on the safety of 37 compounds belonging to different chemical groups, when used as sensory additives (flavourings) in feed for all animal species formerly assessed by the Panel in the context of the re-evaluation of these feed additives. The FEEDAP Panel concludes that ethyl oleate [09.192] and benzyl cinnamate [09.738] are safe at the proposed use level of 5 mg/kg complete feed for all animal species, the consumer and the environment; ethyl salicylate [09.748] is safe up to the maximum proposed use level of 5 mg/kg complete feed for all animal species and the consumer. No new data were submitted on the safety for the user that would allow the FEEDAP Panel to change its previous conclusion for 26 out of the 37 compounds under assessment. The use of 4-terpinenol [02.072], linalyl butyrate [09.050], linalyl formate [09.080], linalyl propionate [09.130], linalyl isobutyrate [09.423], isopulegol [02.167] and 1,2-dimethoxy-4-(prop-1-enyl)-benzene [04.013] as flavouring additives at the proposed use level of 5 mg/kg in feed for all animal species is considered safe for the environment. The use of 3-methyl-2-cyclopenten-1-one [07.112] at 0.5 mg/kg and methyl dihydrojasmonate [09.520] at 5 mg/kg in feed for all animal species except marine animals is considered safe for the environment. © 2022 Wiley‐VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KgaA on behalf of the European Food Safety Authority.
ELLIS HL, JACOBSON J. Benzyl cinnamate (Jacobson's solution) with vitamin A. A one-year experience in the treatment of cerebrovascular lesions. Harlem Hosp Bull (N Y). 1960 Mar;1:97-102. PMID: 13820044.
Bhatia SP, Wellington GA, Cocchiara J, Lalko J, Letizia CS, Api AM. Fragrance material review on benzyl cinnamate. Food Chem Toxicol. 2007;45 Suppl 1:S40-8. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2007.09.027.
Abstract. A toxicologic and dermatologic review of benzyl cinnamate when used as a fragrance ingredient is presented.
SCAL JC. Benzyl cinnamate in treatment of Ménière's syndrome and tinnitus aurum; a clinical report. Eye Ear Nose Throat Mon. 1946 Mar;25:150. PMID: 21027078.
| Evaluate |
