| "Description" by Al222 (24142 pt) | 2025-May-21 10:48 |
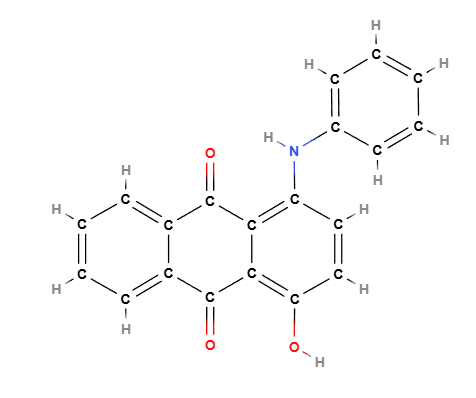
1-Anilino-4-hydroxyanthraquinone
also known as CI 60724 or Disperse Violet 47, is a liposoluble anthraquinone dye with a deep violet color, belonging to the solvent dye class. It is known for its exceptional thermal and photostability, making it ideal for a wide range of cosmetic and industrial applications, especially in anhydrous or oily formulations..
1. Chemical structure and molecular composition
Molecular formula: C₂₀H₁₃NO₃
Molar mass: ~315.32 g/mol
Core structure: anthraquinone (three-ring system with carbonyl groups at positions 9 and 10)
Substituents:
Anilino group (–NH–C₆H₅) at position 1
Hydroxyl group (–OH) at position 4
These substitutions extend π-conjugation and are responsible for the compound’s strong violet absorption in the visible spectrum, as well as its lipophilicity.
2. Spectroscopic and photophysical properties
λmax (absorption peak): ~550–590 nm (depending on solvent)
UV-Vis behavior: highly stable, minimal degradation under UV or oxidative stress
Fluorescence: none or very weak
Shade: varies from bluish violet to dark magenta depending on solvent polarity
3. Physical properties and solubility
Appearance: dark violet crystalline powder
Melting point: ~205–215 °C
Solubility:
Insoluble in water
Soluble in oils (mineral, vegetable), esters, alcohols, silicones, and organic solvents
Thermal and chemical stability:
Stable at high temperatures (>180 °C)
Resistant to light, UV radiation, oxidation, and pH variation (up to ~pH 9)
4. Industrial synthesis
Typically synthesized through:
Anilination of anthraquinone
Followed by hydroxylation in the desired position
Final purification via crystallization or vacuum distillation
The resulting dye is high-purity, storage-stable, and offers consistent color performance.
5. Primary applications
a. Cosmetics
Used in:
Lipsticks, lip balms, lip liners
Oil-based perfumes, color balms, waterproof make-up
Formulations based on silicones, waxes, or anhydrous oils
Labeled in INCI lists as CI 60724, it is used in concentrations from 0.01% to 0.3%.
b. Industrial
Colored waxes (for leather, wood, and furniture)
Lubricants and mineral oils (as colorants or tracers)
Plastics (e.g., PVC, polyethylene, polystyrene)
Fuels (in select markets as a tracer dye)
Inks, permanent markers, and dyes for synthetic fibers
6. Regulatory status and safety
Not approved for food or ophthalmic use
Allowed for external use in cosmetics (not for lips or mucosal areas in some regions)
Must meet strict purity criteria to avoid traces of secondary aromatic amines
EU (Reg. 1223/2009): approved for external use with restrictions
US (FDA): not approved for food, lip, or eye products
Toxicology
Non-carcinogenic, non-mutagenic, non-sensitizing at cosmetic levels
Low dermal absorption, especially in oily systems
Well tolerated in patch tests and in vitro assays
7. Environmental impact
Non-biodegradable, but used at very low concentrations
Not volatile, low risk of environmental bioaccumulation
Requires proper disposal in industrial use due to synthetic origin
8. Conclusion
1-Anilino-4-hydroxyanthraquinone (CI 60724) is a highly stable violet anthraquinone dye, ideal for anhydrous and oil-based cosmetic products as well as technical applications. Its color strength, resistance to degradation, and broad solvent compatibility make it a preferred choice in decorative cosmetics and industrial formulations where a long-lasting, vibrant violet tone is desired.
 |  |
Molecular Formula C20H13NO3
Molecular Weight 315.3 g/mol
CAS 19286-75-0
UNII BN3Q055JL5
EC Number 242-939-0
Synonyms:
Disperse violet 27
Disperse Violet 23
CI 60724
1-Hydroxy-4-anilinoanthraquinone
1-Anilino-4-hydroxyanthraquinone
References__________________________________________________________________________
Lorenzon, V., & Faccio, G. (2022). Tackling Colorants Sustainability Combining Disruptive Science and Sustainable Leadership: A Review Article. Colorants, 1(4), 400-410.
Abstract. Many pigments and dyes are not only valuable molecules in manufacturing, but also environmental pollutants. Stemming from the observation of the slow pace of change taking place to counter the ‘fast fashion’ phenomenon and its environmental consequences, this critical review highlights the importance not only of biotechnological approaches but also of a sustainable leadership to achieve a future-proof fashion industry. Science has been producing sustainable alternatives to counter the issue of dyes, but this is not enough. A change in the business attitude and leadership approach of the organizations that operate in the industry is needed. Only through the successful combination of new technologies and forward-looking decision-making will it be possible to alter the status quo and deal with the multiple environmental challenges that businesses are and will be facing.
Naiki, K. (1959). Studies on Disperse Dyes (XVI) Dyeability and Fastness of Aminoanthraquinones. Sen'i Gakkaishi, 15(3), 203-208.
Abstract. Eighty-nine disperse dyes of aminoanthraquinone series were synthesized and their dyeability and fastness were examined. Relationship between structure and dyeability is discussed in terms of a/o and molecular size of dye. The a/o (inorganic property/organic property) is calculated by the use of Fuijita's conceptional diagram. The a/o is equivalent to hydrophility/hydrophobity. The average a/o value of dyes, having good dyeability on acetate, is about 1.25 and this is consistent with that of secondary cellulose acetate. It seems that the molecular size of dyes which can diffuse into cellulose acetate is less than about 13 Å in normal dyeing process. The light fastness of dyes decreases in the following order. 1-Amino-4-hydroxyanthraquinones>1, 4-Diaminoanthraquinones>1, 4, 5-Triamino-8-hydroxyanthraquinones>1-Aminoanthrquinones>1, 4, 5, 8-Tetraminoanthraquinones. An electron attractive N-substituent, such as β-chloroethoxycarbonyl group, increases the light fastness and an electron donating group, such as β-hydroxyethyl group, decreases the light fastness. It seems that the a/o ratio of dyes, having poor wash fastness, is more than 1.25, and the molecular size of the dyes is less than about 11.0Å.
| Evaluate |
