| "Descrizione" by Frank123 (12488 pt) | 2023-Apr-28 19:33 |
Review Consensus: 8 Rating: 8 Number of users: 1
| Evaluation | N. Experts | Evaluation | N. Experts |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | ||
| 2 | 7 | ||
| 3 | 8 | ||
| 4 | 9 | ||
| 5 | 10 |
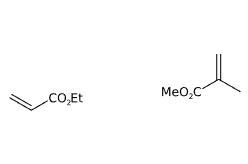
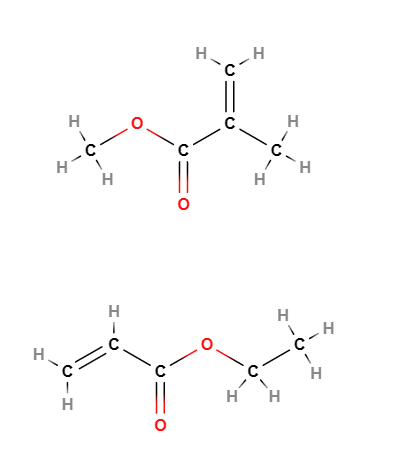
E1206 Neutral Methacrylate Copolymer (NMC) is a chemical compound produced by a process of emulsion polymerisation of the monomers ethyl acrylate and methyl methacrylate and subsequent purification by steam distillation. Filtration is carried out to remove residual monomers.
It appears in the form of a white powder.

What it is used for and where
Food
Ingredient included in the list of European food additives as E1206 as a glazing agent in solid food supplements and solid foods for special medical purposes
Medical
Neutral Methacrylate Copolymer is a fully polymerised copolymer used in the pharmaceutical industry to enable the delayed release of active ingredients (1).
Safety
EFSA's Panel on Food Additives and Nutrient Sources Added to Food assessed in 2010 that for Neutral Methacrylate Copolymer, chronic effects on the gastrointestinal tract after oral administration cannot be excluded, however, its use in solid food supplements at the proposed levels of use and usage does not raise safety concerns (2).
A subsequent study in 2020 (FAO/WHO) confirmed the conclusions of the previous study by noting that dietary exposure assessments of methyl methacrylate and ethyl acrylate due to their residual presence in NMC methacrylate and ethyl acrylate due to their residual presence in NMC suggest that exposure to these monomers from NMC use is not a safety concern (3).
 |  |
 |  |
- Molecular Formula C10H16O4
- Molecular Weight 200.23
- CAS 9010-88-2
- UNII XRK36F13ZZ
- EC Number 618-459-6
Synonyms:
- ethyl acrylate methyl methacrylate polymer
- Ethyl acrylate methyl methacrylate
- methyl methacrylate ethyl acrylate polymer
References_____________________________________________________________________
(1) Eisele, J., Haynes, G., Kreuzer, K. and Rosamilia, T., 2013. Characterisation and toxicological assessment of Neutral Methacrylate Copolymer for GRAS evaluation. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, 67(3), pp.392-408.
Abstract. Neutral Methacrylate Copolymer is a fully polymerised copolymer used in the pharmaceutical industry to permit pH-independent delayed release of active ingredients from oral dosage forms. This function has potential use with food supplements and this article describes available information on the safety of the substance. Oral administration of radiolabelled copolymer to rats resulted in the detection of chemically unchanged copolymer in the faeces, with negligible absorption. Safety studies revealed no adverse toxicity following repeated administration at doses of up to 2000 mg/kg bw/d in a sub-chronic study in rats or 250 mg/kg bw/d in a sub-chronic study in dogs. No reproductive toxicity occurred at up to 2000 mg/kg bw/d in rats or rabbits. The substance shows no evidence of genotoxicity, has low acute toxicity and no irritation or sensitisation potential. An ADI value of 20 mg/kg bw was concluded from two alternative approaches. Daily exposure from use in dietary supplements is estimated as up to 10.0 mg/kg bw in adults and 13.3 mg/kg bw in children. There would therefore appear to be no safety concerns under the intended conditions of use. The information provided is intended to support an evaluation that the substance may be “generally recognized as safe” (GRAS).
(2) EFSA Panel on Food Additives and Nutrient Sources added to Food (ANS), 2010. Scientific Opinion on the safety of neutral methacrylate copolymer for the proposed uses as a food additive. EFSA Journal, 8(7), p.1655.
Abstract. The Panel on Food Additives and Nutrient Sources added to Food provides a scientific opinion on the use of neutral methacrylate copolymer (NMC, a 30% dispersion of the dry copolymer in water) as a glazing agent in solid food supplements and solid foods for special medical purposes (FSMPs). The dispersion contains 0.7% of polyethylene glycol monostearyl ether, which is not a authorised food additive; the opinion does not include a safety evaluation of this substance. From studies on metabolism/toxicokinetics, acute and subchronic oral toxicity, genotoxicity, and developmental toxicity it is concluded that NMC is essentially not absorbed and that any absorbed material is not retained in the tissues. No data on reproductive toxicity, chronic toxicity and carcinogenicity are provided. In the absence of such data, chronic effects on the gastrointestinal tract following oral administration cannot be excluded. Therefore, the Panel considers that an ADI should not be established and that a margin of safety (MOS) approach is appropriate. Data from in vitro Ames and mammalian cell mutation assays and an in vivo micronucleus assay show that NMC does not raise concern with respect to genotoxicity. The calculated anticipated exposure (coating level 200 mg/tablet) to NMC from both its proposed use in food supplements and its approved use in pharmaceuticals is 46.7 mg/kg bw/day for high consumer adults, and 32 mg/kg bw/day for children. Two subchronic toxicity studies in rats and a developmental study in rabbits revealed NOAELs of 2000 mg/kg/bw/day (highest dose level tested) resulting in a MOS of at least 43 for adults and at least 63 for children. The Panel considers these margins of safety sufficient given the lack of absorption and that the exposure estimates are based on worst case assumptions. The Panel concludes that the use of NMC in solid food supplements at the proposed use and use levels is not of safety concern. The Panel could not assess the safety of neutral methacrylate copolymer for uses in solid foods for special medical purposes.
(3) World Health Organization, 2020. Safety evaluation of certain food additives: prepared by the eighty-sixth meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA).
| Evaluate |
