| "Descrizione" by FRanier (10033 pt) | 2025-Oct-29 17:05 |
Review Consensus: 10 Rating: 10 Number of users: 1
| Evaluation | N. Experts | Evaluation | N. Experts |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | ||
| 2 | 7 | ||
| 3 | 8 | ||
| 4 | 9 | ||
| 5 | 10 |
Dextrose (Glucose) is a monosaccharide, polyhydroxyaldehyde, the main source of carbon for cell biosynthesis and energy generation in the human body. It is a six-carbon-atom sugar containing an aldehyde group and is the predominant monosaccharide in living organisms. Its primary function is to provide the body with energy.
Excess fat accumulation in metabolic organs, impaired glucose homeostasis and the development of insulin resistance are hallmarks of type 2 diabetes mellitus. The liver plays a key role in coordinating systemic metabolic homeostasis and adaptation to nutrient availability and deprivation (1).
Understanding the mechanisms that regulate insulin-stimulated glucose uptake by skeletal muscle is important because muscle insulin resistance is a key defect in the progression to type 2 diabetes mellitus. Even in non-diabetic individuals, insulin resistance increases the risk of atherogenesis, cardiovascular disease, hypertension, cognitive dysfunction and some cancers (2).
Glucose was used in the form of an ultrasound-guided hypertonic injection in patients with chronic shoulder pain and supra-spinous tendinopathy and was able to provide relief from pain, disability and shoulder range of motion for up to 2 weeks after surgery (3).
The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of dextrose gel in the management of neonatal hypoglycaemia in postnatal wards. Conclusions: dextrose gel has been shown to be effective in the management of neonatal hypoglycaemia in the postnatal environment, reducing admission to the neonatal intensive care unit and mother-baby separation (4).
Industrially it appears as a white powder soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol, insoluble in ether.

What it is used for and where
Food
It is a sugar, but not as sweet-tasting as sucrose and is produced from starch by glucanase saccharification, amylase liquefaction, refining, concentration and drying processes. It is extracted with water and methanol.
Medical
Nutritional agent and used in the production of calcium gluconate and vitamin C
Other uses
- Wastewater treatment
- Microbial fermentation
- Reducing agent printing, tanning, dyeing, glass industries
- Organic crops
- Suitable for formulations such as phosphorus, molybdenum, silicon, tungsten, nitrite, etc.
- Corrosion inhibitor in closed water circulation circuits
The most relevant studies on this ingredient have been selected with a summary of the contents:
Typical commercial product characteristics Glucose
| Appearance | Crystalline powder |
| pH | 6.0~6.5 |
| Boiling Point | 527.1±50.0°C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 146°C |
| Flash Point | 286.7±26.6 °C |
| Vapor pressure | 0.0±3.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Refraction Index | 1.573 |
| PSA | 118.22000 |
| LogP | -3.17 |
| Specific rotation | 52.0~53.5 |
| Sieve Analysis | 100% pass 80 mesh |
| Total Plate Count | 1000/g Max |
| Yeast & Mold | 100/g Max |
| Sulphate ash | ≤0.05 |
| Chloride | ≤0.01 |
| Arsenic | ≤1ppm |
| Lead | ≤2ppm |
| Cadmium | ≤1ppm |
| Hygrargyrum | ≤0.1ppm |
| Shelf life | 2 years |
 |  |
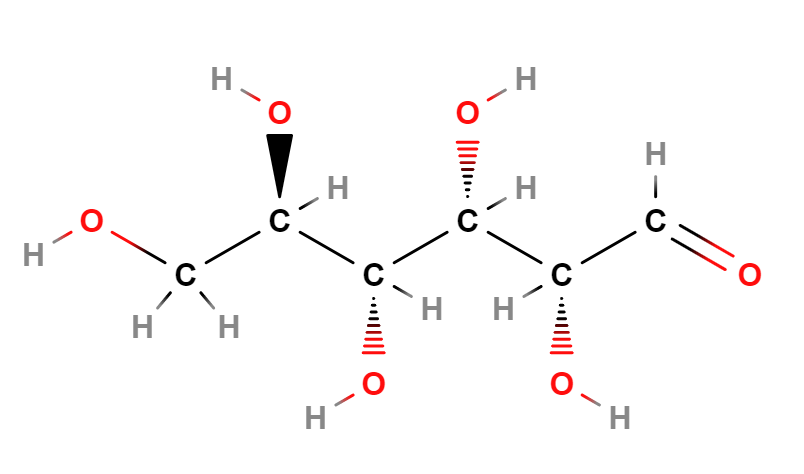 |  |
- Molecular Formula C6H12O6
- Peso molecolare 180.156
- Exact Mass 180.063385
- CAS 50-99-7
- UNII 5SL0G7R0OK
- EC Number 200-075-1
- DSSTox Substance ID DTXSID4048729
- IUPAC (2R,3S,4R,5R)-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanal
- InChl=1S/C6H12O6/c7-1-3(9)5(11)6(12)4(10)2-8/h1,3-6,8-12H,2H2/t3-,4+,5+,6+/m0/s1
- InChl Key GZCGUPFRVQAUEE-SLPGGIOYSA-N
- SMILES C(C(C(C(C(C=O)O)O)O)O)O
- MDL number MFCD00063774
- PubChem Substance ID 24894295
- ChEBI 42758
- RTECS LZ6600000
- NCI C61716
- ICSC 0865
- RXCUI 349730
- Beilstein 1724615
- NACRES NA.21
Synonyms:
D-Glucose; D-(+)-Glucose: (2R,3S,4R,5R)-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanal
References__________________________________________________________________
Abstract. Background: Rotator cuff lesions are common causes of shoulder pain. Although patients with symptoms caused by chronic rotator cuff tendinopathy can be treated using conservative treatments, some of them may still experience refractory symptoms. Hypertonic dextrose prolotherapy (DPT) may be another treatment choice for these refractory symptoms. Aim: The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of an ultrasound-guided hypertonic dextrose injection for patients with chronic supraspinatus tendinopathy. Design: Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Setting: Academic medical center. Population: Outpatients patients (N.=31) with chronic supraspinatus tendinopathy and shoulder pain for more than six months. Methods: Study group treated with one dose of an ultrasound-guided hypertonic dextrose (20%) injection at the supraspinatus enthesis site, whereas control patients received one dose of 5% normal saline through the same method. The Visual Analog Scale (VAS), Shoulder Pain And Disability Index (SPADI), shoulder active range of motion (AROM) and ultrasonographic thickness and histogram results of the supraspinatus tendon were evaluated before intervention and at two and six weeks after intervention. The outcome differences between the study and control groups were analyzed by using repeated-measures analysis of variance (ANOVA). Results: In total, 31 patients completed the study. The study group indicated a significant improvement in the VAS (P=0.001), SPADI scores (P=0.017), shoulder AROM of flexion (P=0.039), and abduction (P=0.043) compared with the control group at two weeks after the injection. However, the effect did not sustain until six weeks after the injection. No differences in the histograms and morphological changes (thickness) were noted before and after injection in both groups. Conclusions: This study revealed that the ultrasound-guided hypertonic dextrose injection relieved pain, disability, and improved shoulder AROM for a short period in patients with chronic supraspinatus tendinopathy.
| Evaluate |
