| "Descrizione" by A_Partyns (12953 pt) | 2024-Apr-11 15:01 |
Review Consensus: 10 Rating: 10 Number of users: 1
| Evaluation | N. Experts | Evaluation | N. Experts |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | ||
| 2 | 7 | ||
| 3 | 8 | ||
| 4 | 9 | ||
| 5 | 10 |
Tocopheryl acetate è un composto chimico, lo stesso prodotto di Tocoferolo acetato, ma sintetico, ricavato industrialmente tramite procedimento chimico.
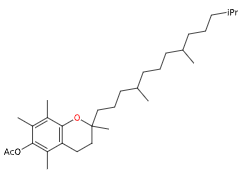
Tocoferolo acetato ([(2R)-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-[(4R,8R)-4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl]-3,4-dihydrochromen-6-yl] acetate) è un prodotto naturale, una forma modificata, idrolizzata, della vitamina E, di difficile ossidazione e con lo stesso colore.
Si presenta in forma di olio dal colore giallastro o come polvere bianca.

A cosa serve e dove si usa
Medicina
E' un potente antiossidante, in pratica una vitamina E. (vedi Vitamina E), ha proprietà sia antiossidanti che antinfiammatorie e può ridurre la crescita batterica locale, promuovendo così la guarigione delle ferite. Liposolubile, aiuta a proteggere i lipidi di membrana dalla perossidazione se assunto per via orale.
Cosmetica
Agente antiossidante. Ingrediente che contrasta lo stress ossidativo e che evita danni cellulari. I radicali liberi, i processi infiammatori patologici, le specie reattive dell'azoto e le specie reattive dell'ossigeno sono responsabili del processo di invecchiamento e di molte malattie causate dall'ossidazione.
Agente condizionante della pelle. Rappresenta il perno del trattamento topico della pelle in quanto ha la funzione di ripristinare, aumentare o migliorare la tolleranza cutanea a fattori esterni, compresa la tolleranza dei melanociti. La funzione più importante dell'agente condizionante è prevenire la disidratazione della pelle, ma il tema è piuttosto complesso e coinvolge emollienti ed umettanti che possono essere aggiunti nella formulazione.
Viene utilizzato in prodotti cosmetici per la pelle, nei dentifrici. E' stato accertato che riduce, dopo l'esposizione ai raggi UV, le scottature solari, agisce anche come umettante quando la vitamina E viene applicata sulla pelle, neutralizza i radicali liberi (1).
Tocoferolo acetato in forma di gel topico unitamente a isotretinoina ha migliorato la sensibilità cutanea e può essere utilizzato come formulazione topica non irritante per il trattamento dell'acne (2).
In una preparazione comprendente alcuni polisorbati, Tween 20, 40, 60 e 80, il Tocoferolo acetato ha dimostrato attività antiossidante in vitro ed efficacia nella rigenerazione della pelle (3).
Sicurezza
Non ha alcuna controindicazione per quanto riguarda la sicurezza. Il gruppo di esperti per i prodotti cosmetici dell'EFSA ha concluso:
"Sulla base delle conoscenze attuali, il SCCNFP ritiene che l'acetato di alfa-tocoferolo non rappresenti una minaccia per la salute dei consumatori e pertanto non propone alcuna restrizione o condizione sull'uso dell'acetato di alfa-tocoferolo nei prodotti cosmetici." (4).
Rischi per la salute respiratoria. La preoccupazione più importante che riguarda l'acetato di vitamina E è emersa dalla sua associazione con EVALI (E-cigarette or Vaping product use-Associated Lung Injury). Il CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) ha identificato l'acetato di vitamina E come una sostanza chimica di preoccupazione tra le persone con EVALI, suggerendo che, quando inalato, può interferire con il normale funzionamento dei polmoni (5).
Per approfondire:
Caratteristiche tipiche ottimali del prodotto commerciale Tocopherol Acetate olio
| Appearance | Yellowish oil |
| Tocopherols | 96.0-102.0 |
| Refractive index | 1.494-1.499 |
| Absorbance E1%1cm | 41-45 |
| Specific rotation | +24° |
| Residue on ignition | ≤0.1 |
| Acidity | ≤0.5 |
| Pb | ≤10 |
| Density | 0.953 g/mL at 25 °C |
| Shelf life | ≥36 months |
 |  |
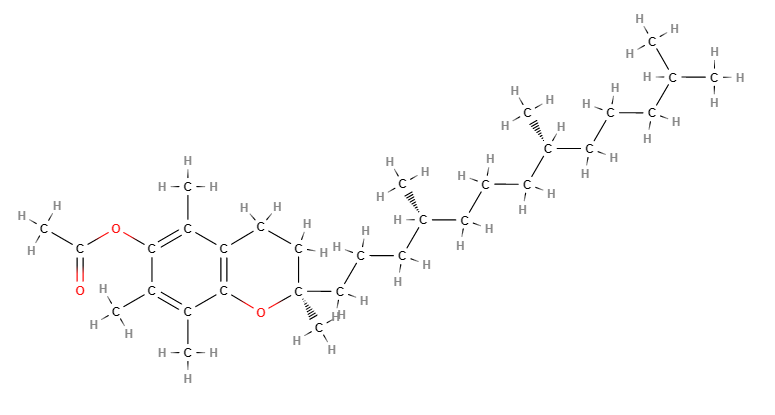 | 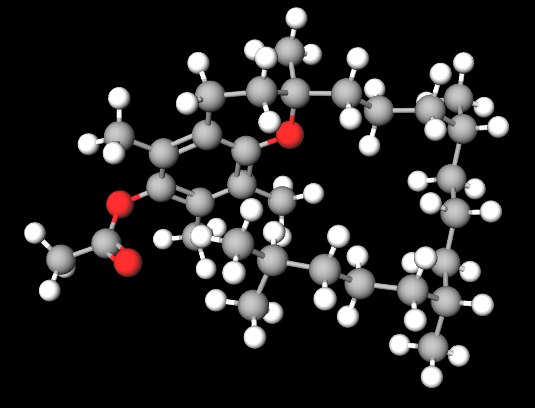 |
- Formula molecolare C31H52O3
- Peso molecolare 472.754 g/mol
- UNII A7E6112E4N
- CAS 58-95-7 12741-00-3 133-80-2 1407-18-7 54-22-8 1406-70-8 26243-95-8 7695-91-2 52225-20-4
- EC Number: 231-710-0 257-757-7 200-405-4
- DSSTox Substance ID DTXSID3021356 DTXSID1031096
- IUPAC [(2R)-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-[(4R,8R)-4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl]-3,4-dihydrochromen-6-yl] acetate
- InChI=1S/C31H52O3/c1-21(2)13-10-14-22(3)15-11-16-23(4)17-12-19-31(9)20-18-28-26(7)29(33-27(8)32)24(5)25(6)30(28)34-31/h21-23H,10-20H2,1-9H3/t22-,23-,31-/m1/s1
- InChl Key ZAKOWWREFLAJOT-CEFNRUSXSA-N
- SMILES CC1=C(C(=C(C2=C1OC(CC2)(C)CCCC(C)CCCC(C)CCCC(C)C)C)OC(=O)C)C
- PubChem Substance ID 24900095 24899940
- MDL number MFCD00072052
- Beilstein Registry Number 97512
- eCl@ss 34058007
- ChEBI 32321
- NACRES NA.79 NA.75
- RTECS GP8280000
Sinonimi:
- Vitamin E acetate
- α-tocopherol acetate
- alpha-Tocopherol acetate
- Tocopheryl acetate
- Alfacol
- Natur-E granulate
- DL-alpha tocopheryl acetate
- (+-)-alpha-Tocopherol acetate
- Ecofrol
- 58-95-7
- Contopheron
- Tofaxin
- Econ
- Covitol 1360
- Vitamin Ealpha acetate
- alpha-Tocopheryl acetate
- DL-alpha-Tocopheryl acetate
- Vitamin E acetate, d-
- DL-alpha-Tocopherol acetate
- 2,5,7,8-Tetramethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-6-cromanyl acetate, (+)-
- 6-Cromanol, 2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-, acetate, (+)-
- 2H-1-Benzopyran-6-ol, 3,4-dihydro-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-, acetate, (2R-(2*(4R*,8R*)))-
- 2H-1-Benzopyran-6-ol, 3,4-dihydro-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-, acetate, [2R-[2R*(4R*,8R*)]]-
- (R,R,R)-.alpha.-Tocopheryl acetate
- 2H-1-Benzopyran-6-ol, 3,4-dihydro-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-, acetate
- 3,4-Dihydro-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-2H-benzopyran-6-yl acetate
- (2R)-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-[(4R,8R)-4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl]-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-6-yl acetate
- 6-Chromanol, 2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-, acetate, (+)-
- (2R)-3,4-Dihydro-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-[(4R,8R)-4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl]-2H-1-benzopyran-6-ol 6-Acetate
- 6-Chromanol, 2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-, acetate
- (2R*(4R*,8R*))-(1)-3,4-Dihydro-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-2H-benzopyran-6-yl acetate
- DL-alpha-Tocopherol acetate, analytical standard
- DL-alpha-Tocopherol acetate, EP/USP/FCC grade
- [(2R)-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-[(4R,8R)-4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl]chroman-6-yl] acetate
- 2H-1-Benzopyran-6-ol, 3,4-dihydro-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-((4R,8R)-4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-, 6-acetate, (2R)-
- 3,4-Dihydro-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-2H-b- enzopyran-6-ol, acetate
- [2R-[2R*(4R,8R*)]]-3,4-Dihydro-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-2H-1-benzopyran-6-ol acetate
- [(2R)-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-[(4R,8R)-4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl]-3,4-dihydrochromen-6-yl] acetate
- [2R*(4R*,8R*)]-()-3,4-dihydro-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-2H-benzopyran-6-yl acetate
- 1406-70-8
- 2H-1-Benzopyran-6-ol, 3,4-dihydro-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-((4R,8R)-4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-, acetate, (2R)-
- 2H-1-Benzopyran-6-ol, 3,4-dihydro-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-((4R,8R)-4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-, acetate, (2R)-rel-
- Ephynal acetate
- Tokoferol acetate
- D-alpha-tocopherol acetate
- Tocopherex
- Evipherol
- Fertilvit
- Tocophrin
- Erevit
- Gevex
- Juvela
- Combinal E
- Tocopheryl acetate
- D-ALPHA-TOCOPHERYL ACETATE
- Epsilan-M
- E-Toplex
- E-Ferol
- Endo E Dompe
- Spondyvit
- (+)-alpha-Tocopherol acetate
- Copherol 1250
- Covitol 1100
Bibliografia___________________________________________________
(1) Teo BS, Basri M, Zakaria MR, Salleh AB, Rahman RN, Rahman MB. A potential tocopherol acetate loaded palm oil esters-in-water nanoemulsions for nanocosmeceuticals. J Nanobiotechnology. 2010 Feb 23;8:4. doi: 10.1186/1477-3155-8-4.
(2) Gupta S, Wairkar S, Bhatt LK. Isotretinoin and α-tocopherol acetate-loaded solid lipid nanoparticle topical gel for the treatment of acne. J Microencapsul. 2020 Dec;37(8):557-565. doi: 10.1080/02652048.2020.1823499.
(3) Caddeo C, Manca ML, Peris JE, Usach I, Diez-Sales O, Matos M, Fernàndez-Busquets X, Fadda AM, Manconi M. Tocopherol-loaded transfersomes: In vitro antioxidant activity and efficacy in skin regeneration. Int J Pharm. 2018 Nov 15;551(1-2):34-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.09.009.
(5) Blount BC, Karwowski MP, Shields PG, Morel-Espinosa M, Valentin-Blasini L, Gardner M, Braselton M, Brosius CR, Caron KT, Chambers D, Corstvet J, Cowan E, De Jesús VR, Espinosa P, Fernandez C, Holder C, Kuklenyik Z, Kusovschi JD, Newman C, Reis GB, Rees J, Reese C, Silva L, Seyler T, Song MA, Sosnoff C, Spitzer CR, Tevis D, Wang L, Watson C, Wewers MD, Xia B, Heitkemper DT, Ghinai I, Layden J, Briss P, King BA, Delaney LJ, Jones CM, Baldwin GT, Patel A, Meaney-Delman D, Rose D, Krishnasamy V, Barr JR, Thomas J, Pirkle JL; Lung Injury Response Laboratory Working Group. Vitamin E Acetate in Bronchoalveolar-Lavage Fluid Associated with EVALI. N Engl J Med. 2020 Feb 20;382(8):697-705. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1916433. Epub 2019 Dec 20. PMID: 31860793; PMCID: PMC7032996.
Abstract. Background: The causative agents for the current national outbreak of electronic-cigarette, or vaping, product use-associated lung injury (EVALI) have not been established. Detection of toxicants in bronchoalveolar-lavage (BAL) fluid from patients with EVALI can provide direct information on exposure within the lung....Vitamin E acetate was associated with EVALI in a convenience sample of 51 patients in 16 states across the United States. (Funded by the National Cancer Institute and others.). Copyright © 2019 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Marrocco A, Singh D, Christiani DC, Demokritou P. E-cigarette vaping associated acute lung injury (EVALI): state of science and future research needs. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2022 Mar;52(3):188-220. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2022.2082918.
Abstract. "E-Cigarette (e-cig) Vaping-Associated Acute Lung Injury" (EVALI) has been linked to vitamin-E-acetate (VEA) and Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), due to their presence in patients' e-cigs and biological samples. Lacking standardized methodologies for patients' data collection and comprehensive physicochemical/toxicological studies using real-world-vapor exposures, very little data are available, thus the underlying pathophysiological mechanism of EVALI is still unknown. This review aims to provide a comprehensive and critical appraisal of existing literature on clinical/epidemiological features and physicochemical-toxicological characterization of vaping emissions associated with EVALI. The literature review of 161 medical case reports revealed that the predominant demographic pattern was healthy white male, adolescent, or young adult, vaping illicit/informal THC-containing e-cigs. The main histopathologic pattern consisted of diffuse alveolar damage with bilateral ground-glass-opacities at chest radiograph/CT, and increased number of macrophages or neutrophils and foamy-macrophages in the bronchoalveolar lavage. The chemical analysis of THC/VEA e-cig vapors showed a chemical difference between THC/VEA and the single THC or VEA. The chemical characterization of vapors from counterfeit THC-based e-cigs or in-house-prepared e-liquids using either cannabidiol (CBD), VEA, or medium-chain triglycerides (MCT), identified many toxicants, such as carbonyls, volatile organic compounds, terpenes, silicon compounds, hydrocarbons, heavy metals, pesticides and various industrial/manufacturing/automotive-related chemicals. There is very scarce published toxicological data on emissions from THC/VEA e-liquids. However, CBD, MCT, and VEA emissions exert varying degrees of cytotoxicity, inflammation, and lung damage, depending on puffing topography and cell line. Major knowledge gaps were identified, including the need for more systematic-standardized epidemiological surveys, comprehensive physicochemical characterization of real-world e-cig emissions, and mechanistic studies linking emission properties to specific toxicological outcomes.
| Evaluate |

